Why use a Burnoff process
They are gaining acceptance in the automotive parts rebuilding industry and more recently in the plastics industry as the most economical method of cleaning metal parts. The emissions from burn-off ovens are quite low and the small amount of ash generated can usually go in the trash. With burn-off ovens environmental impact is minimized and operator safety is maximized.
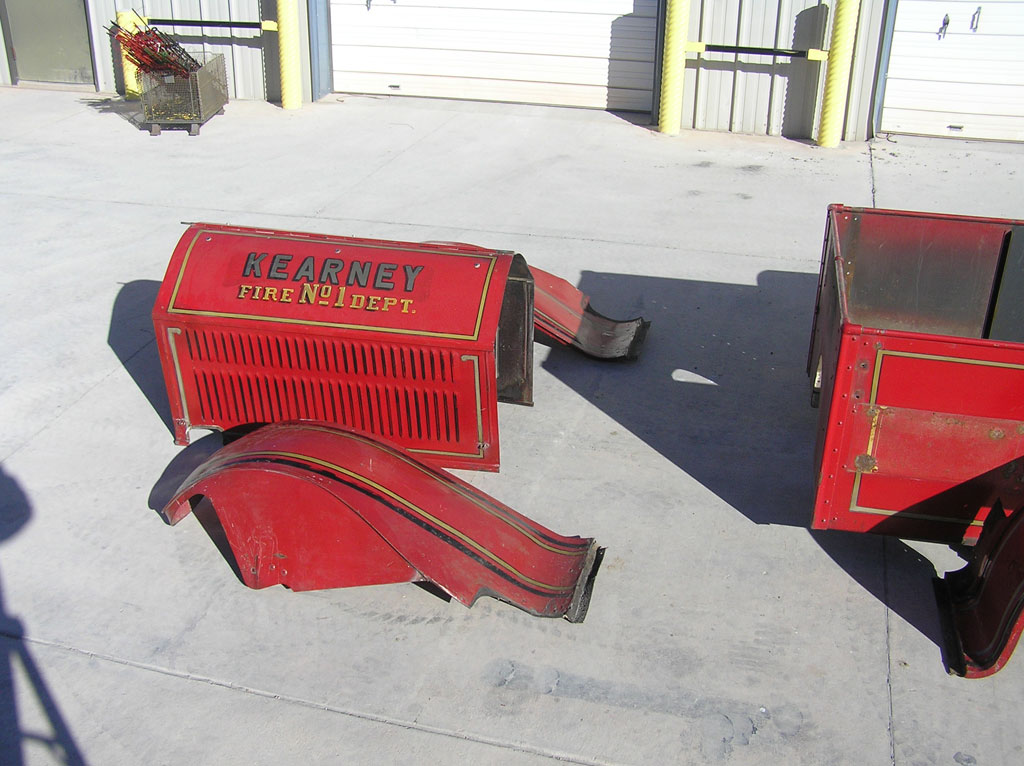
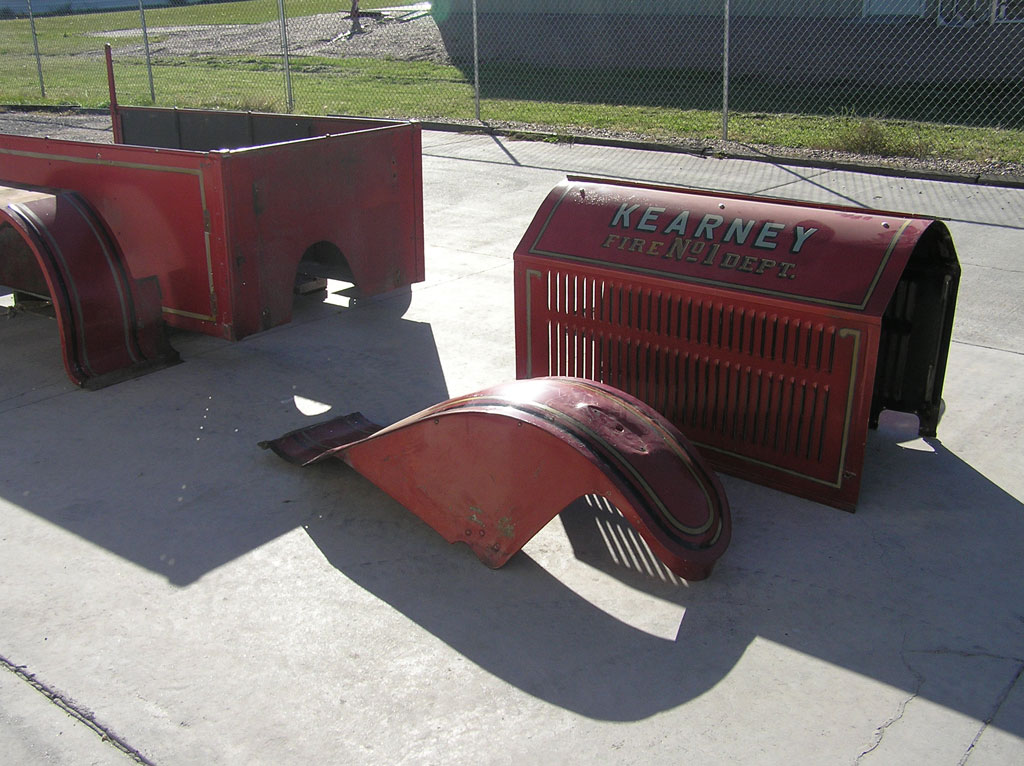
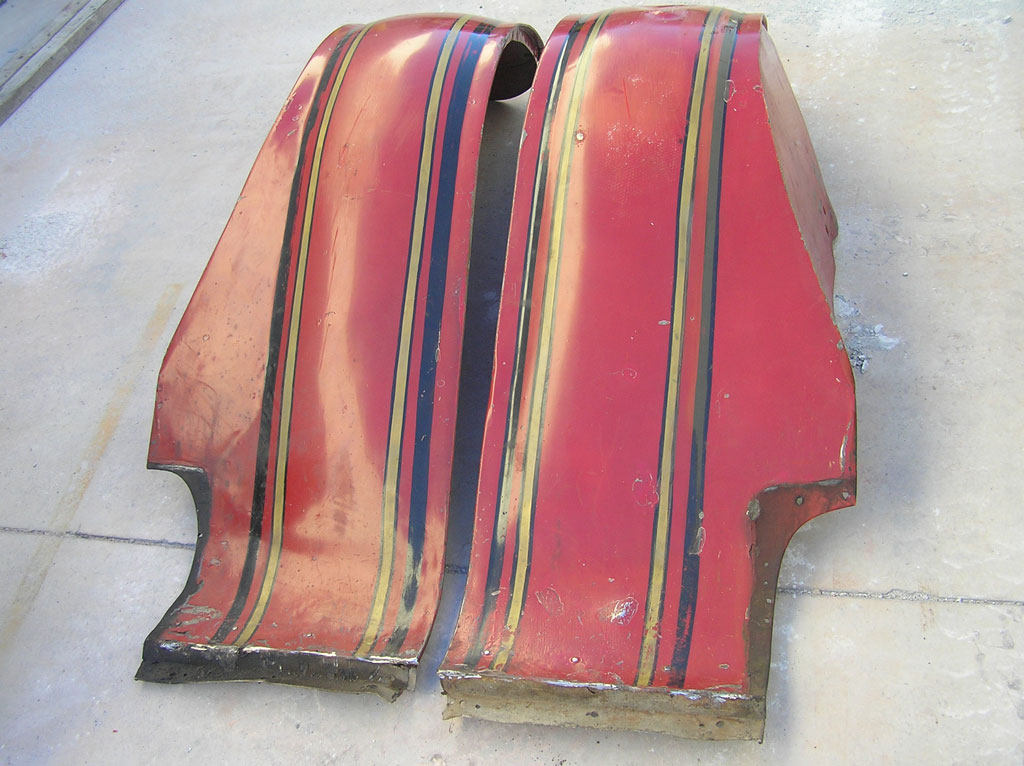
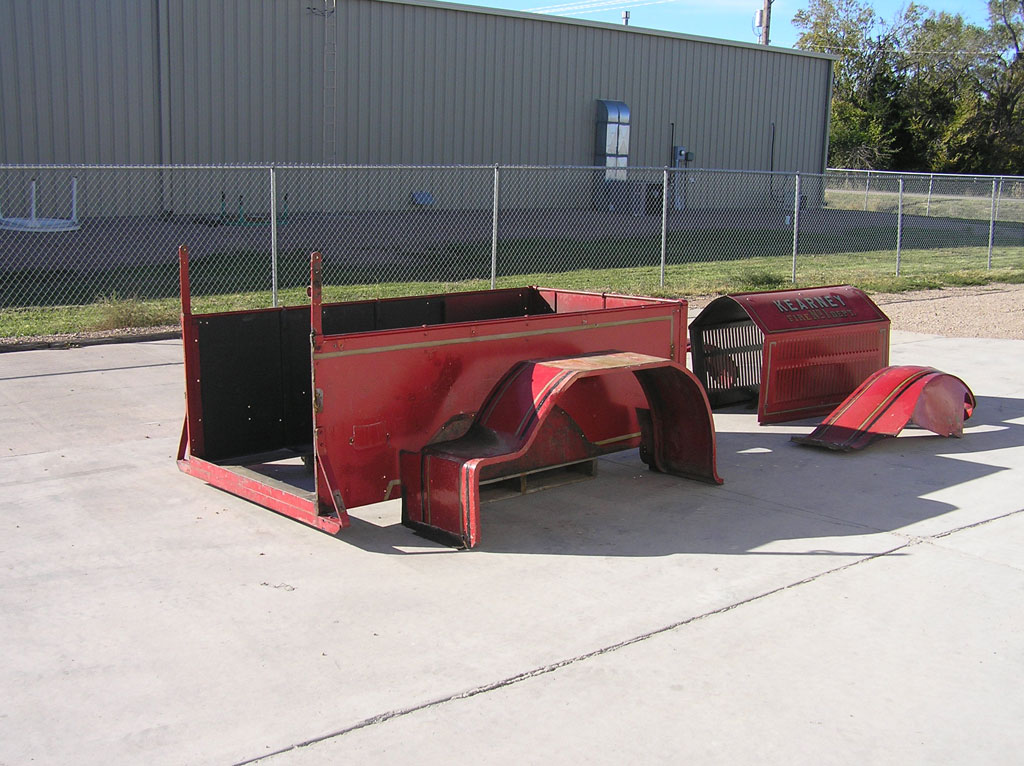
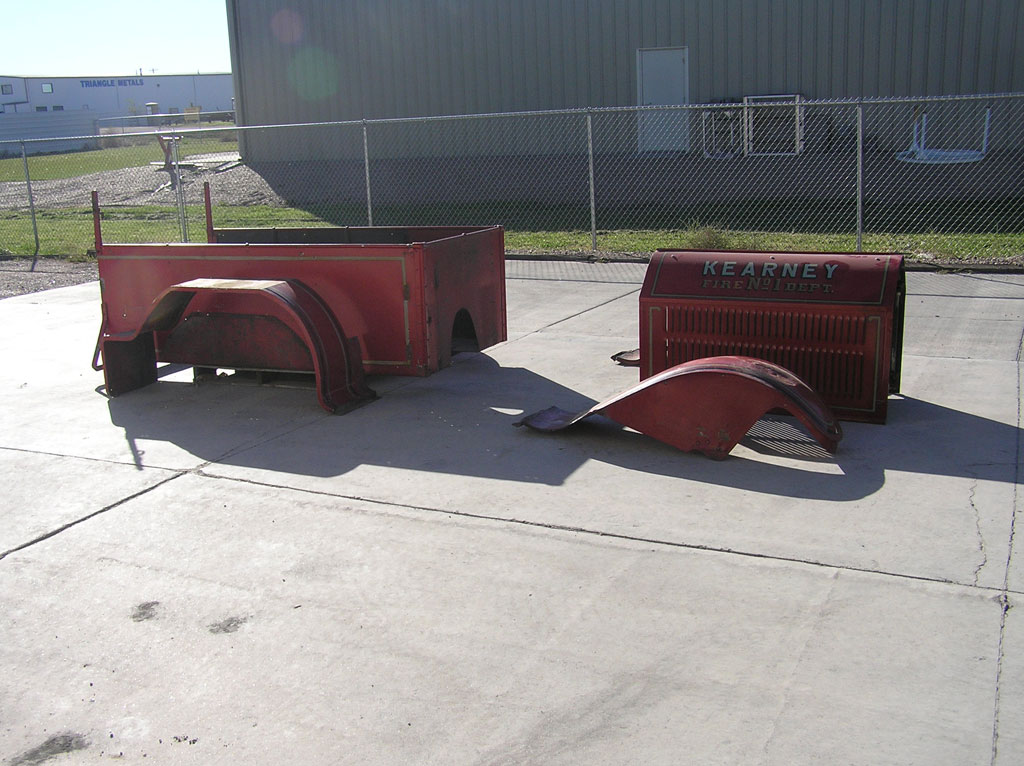
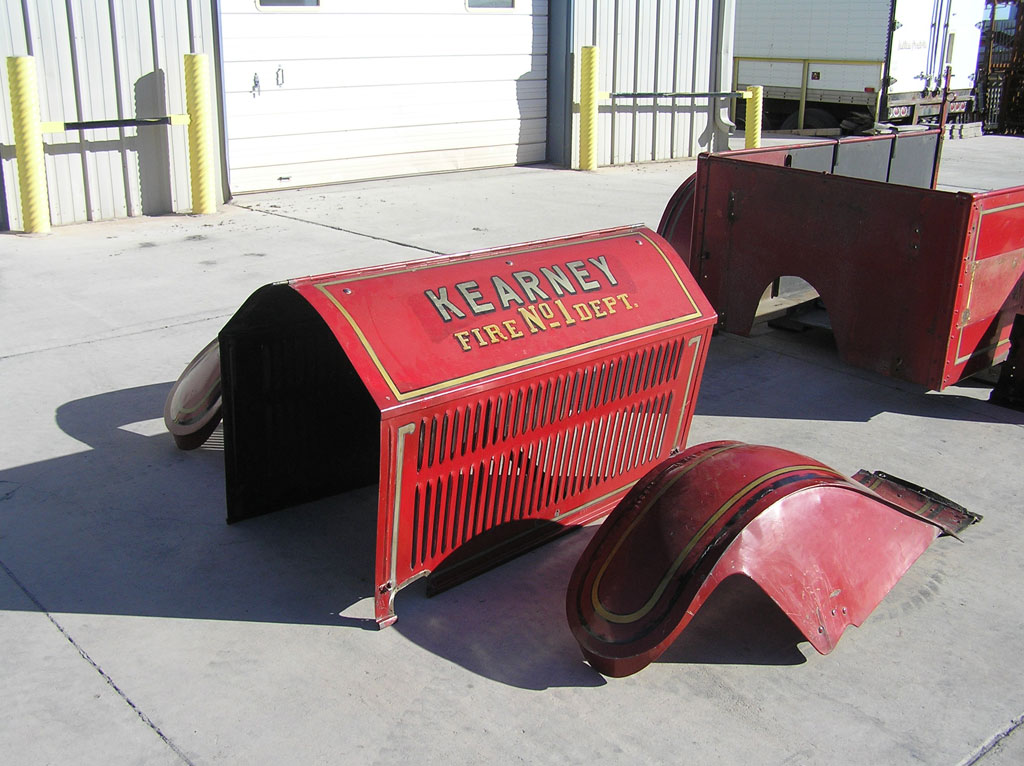
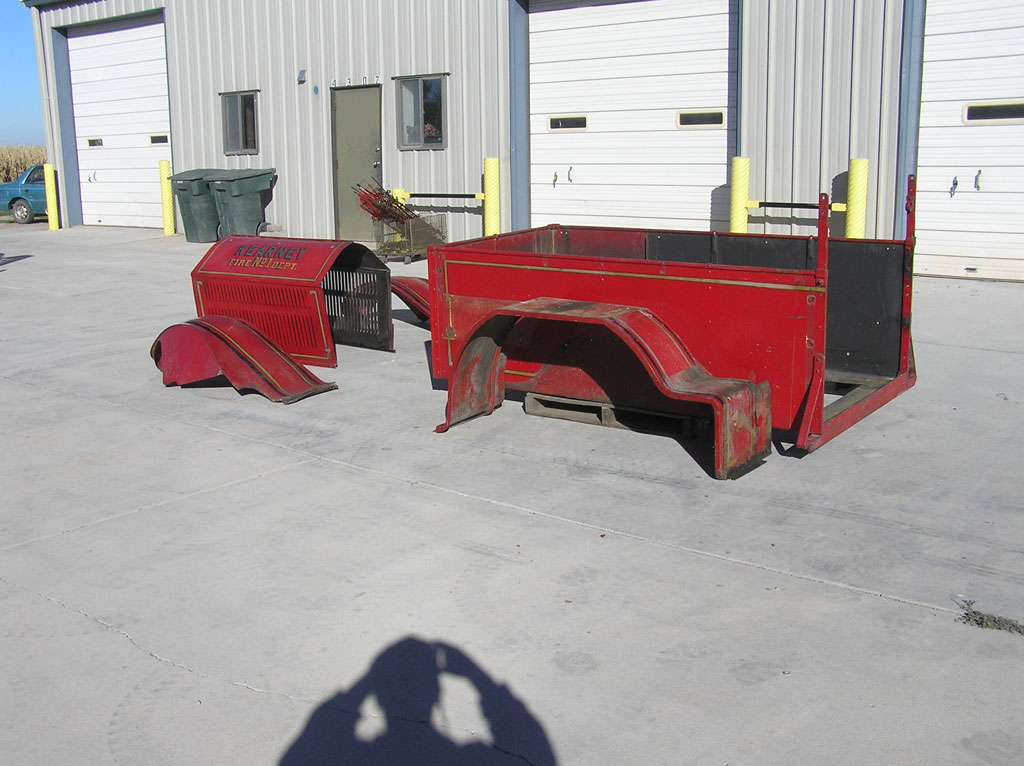
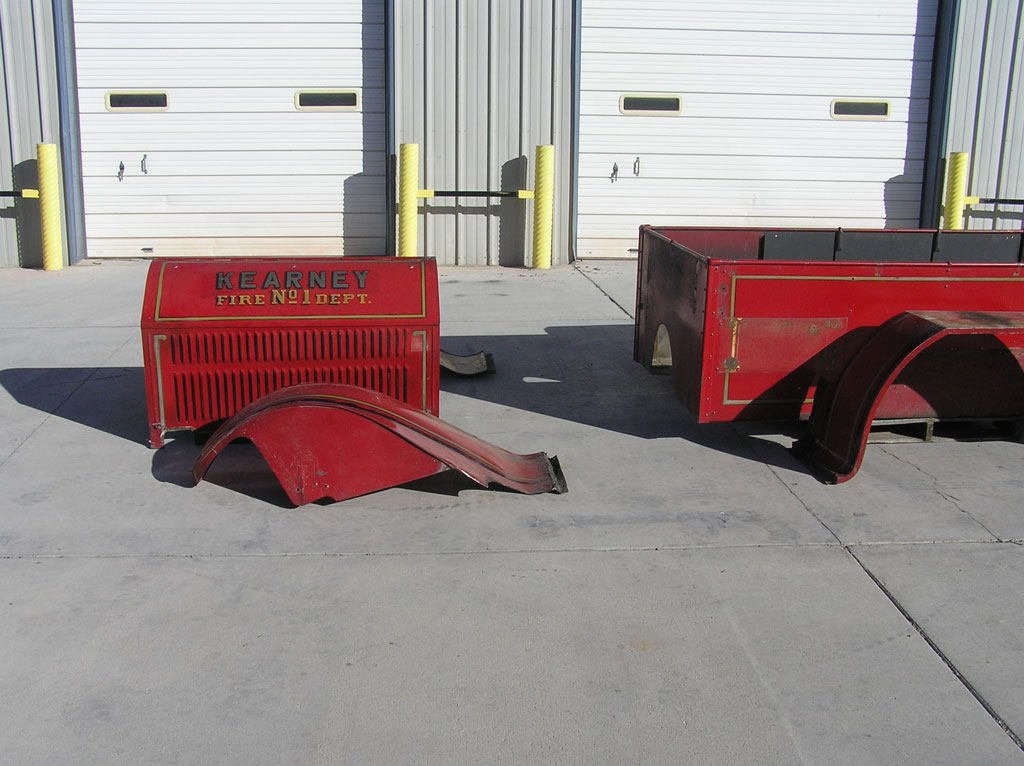
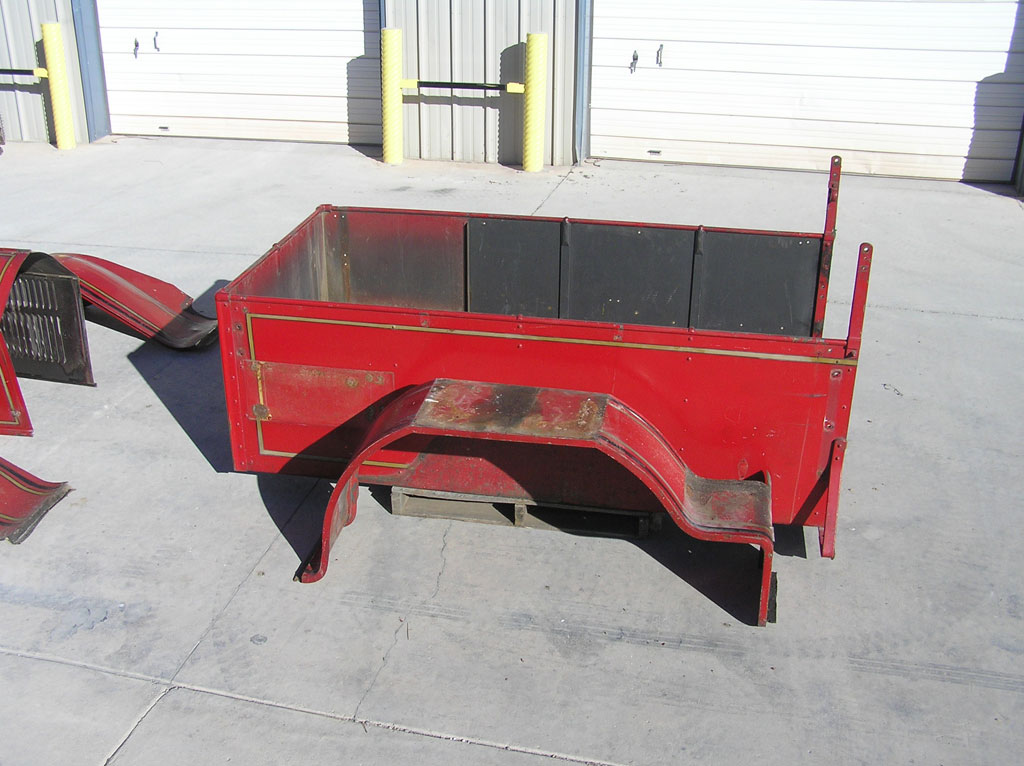
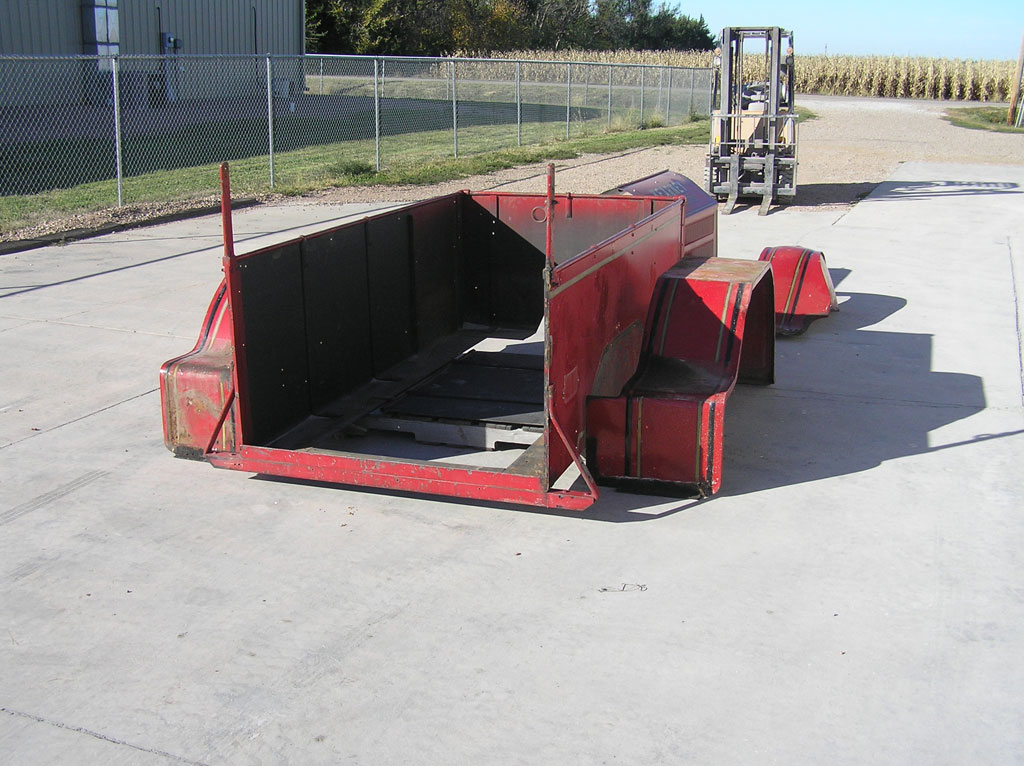
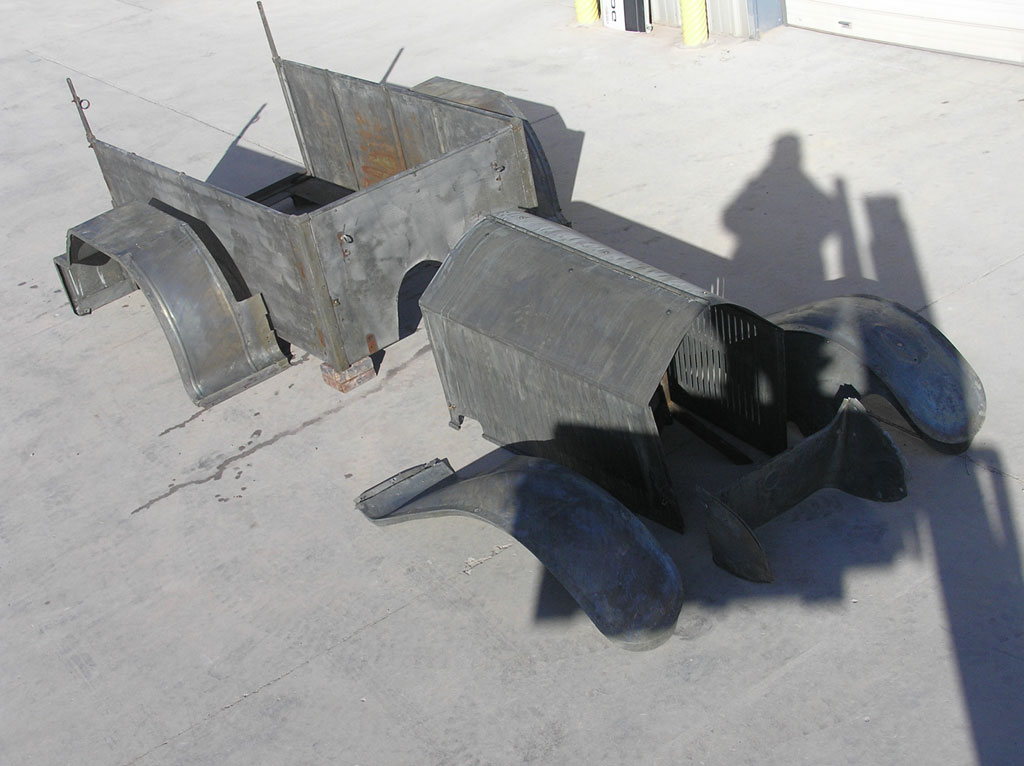
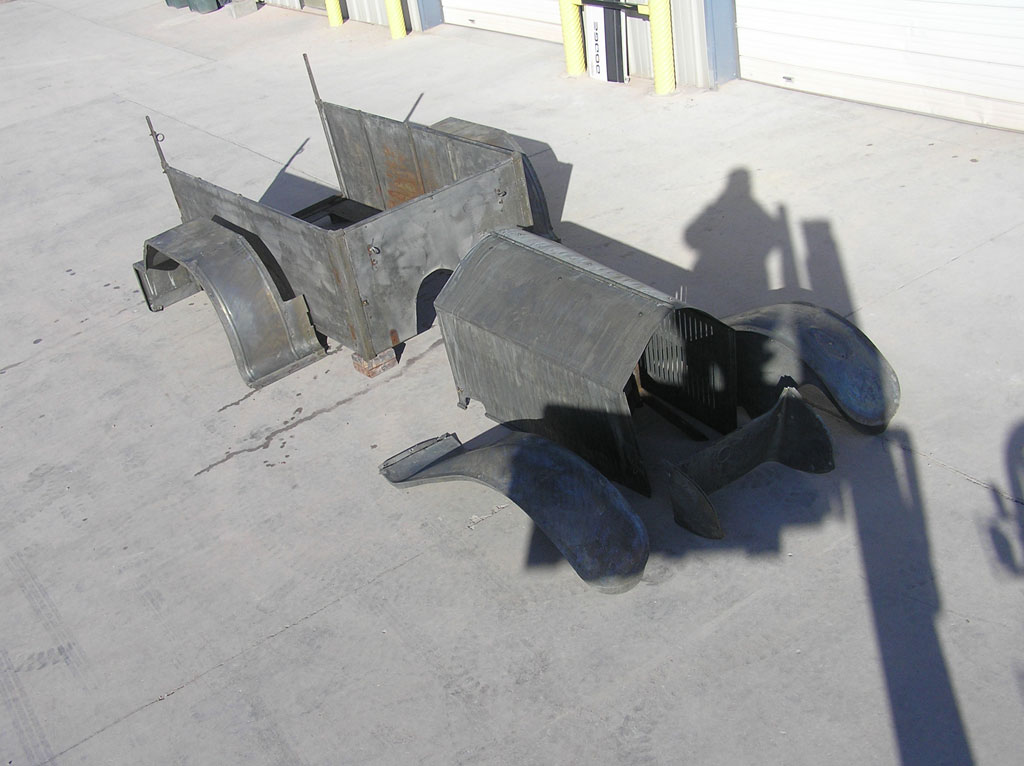
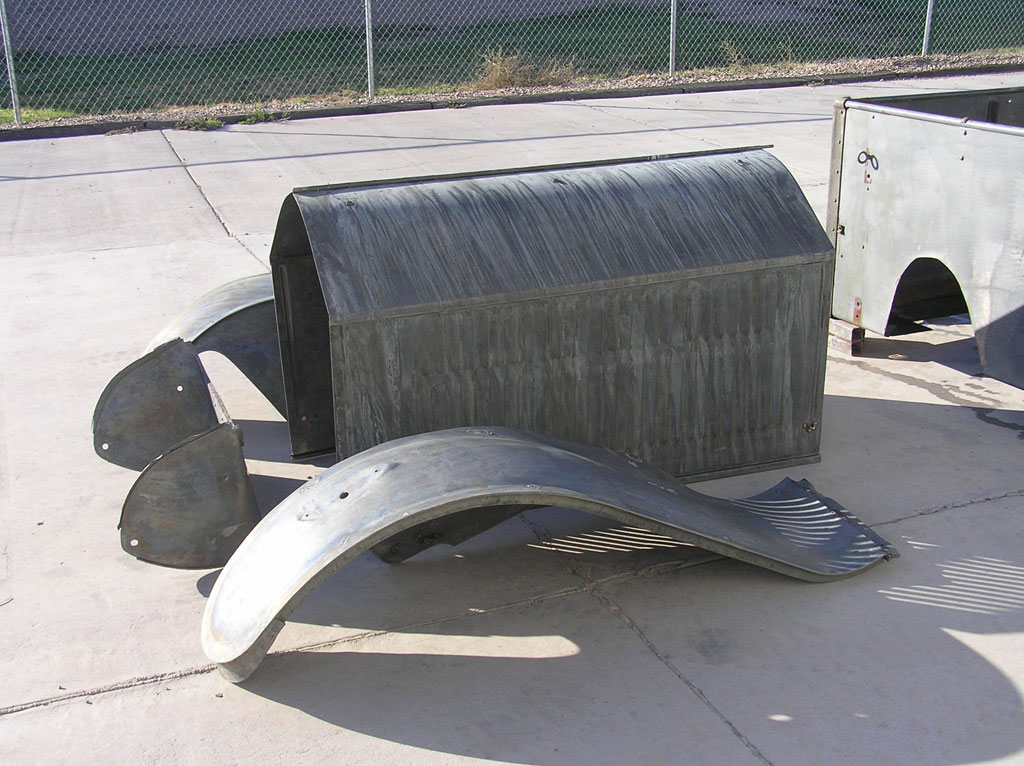
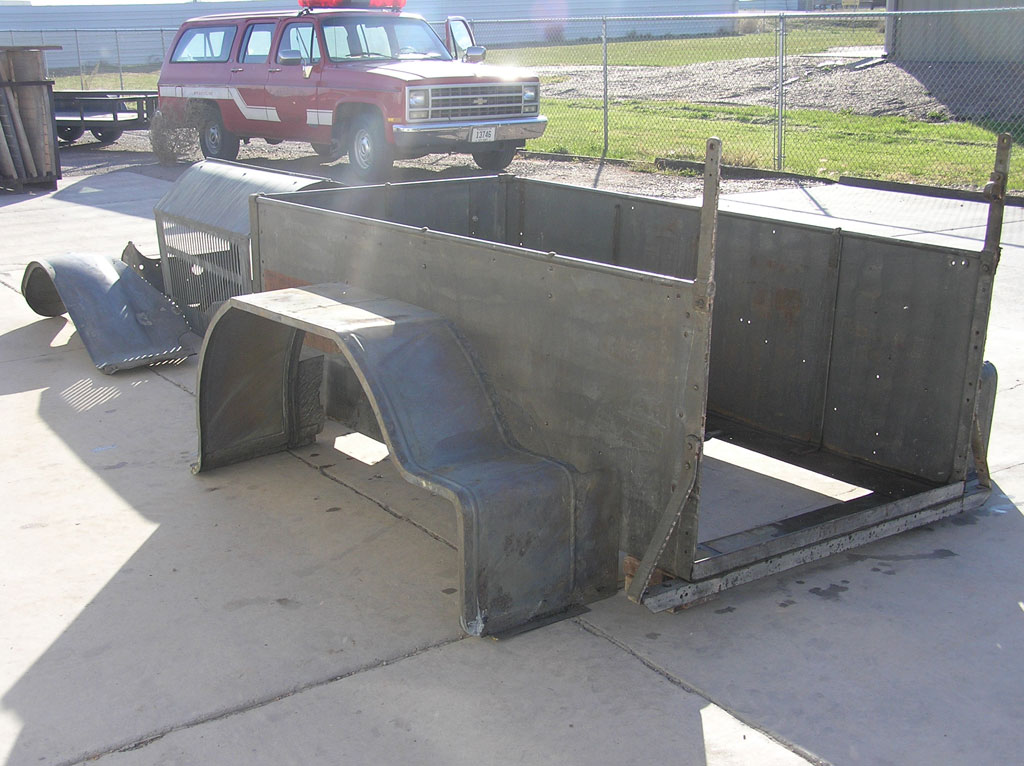
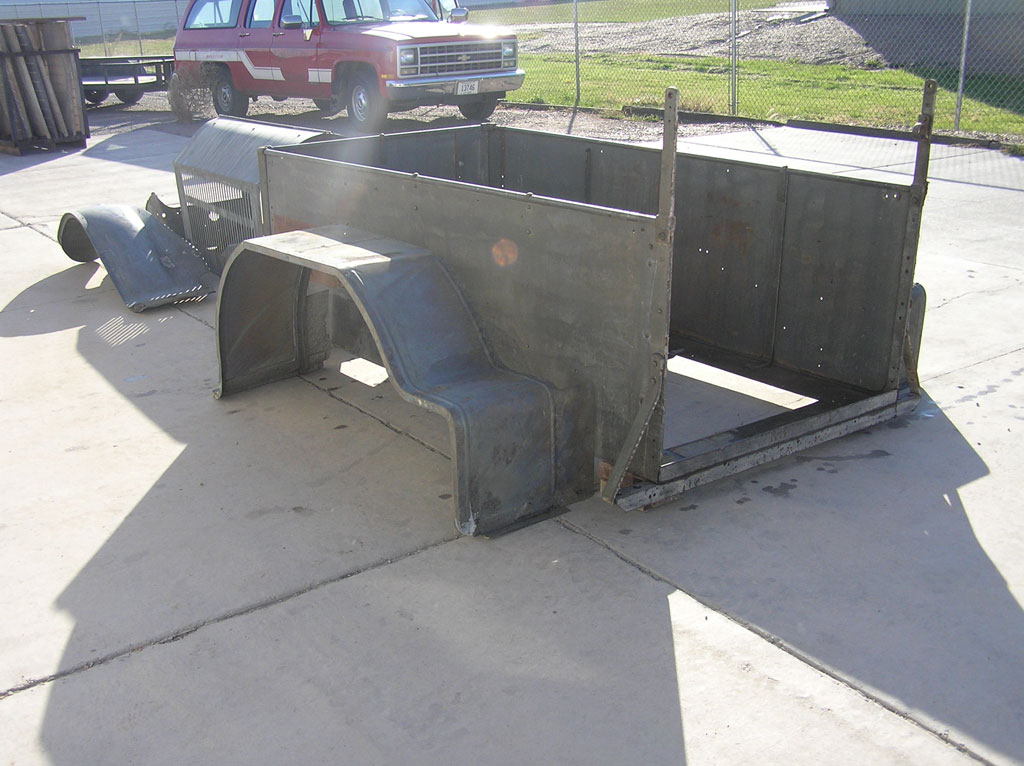
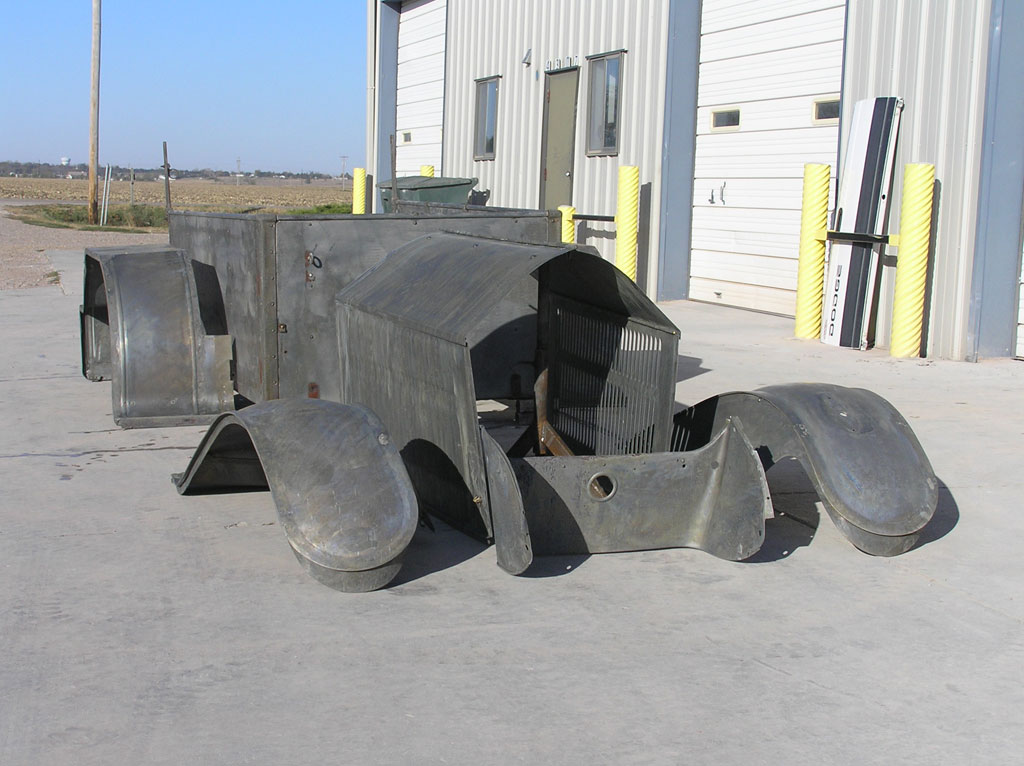
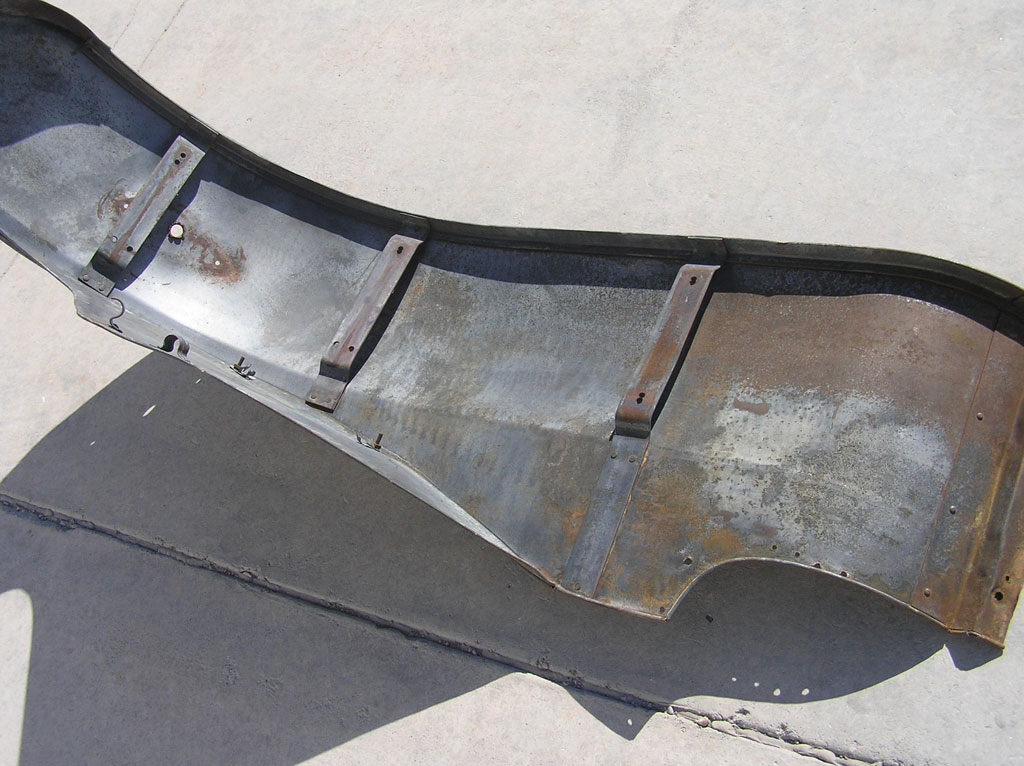
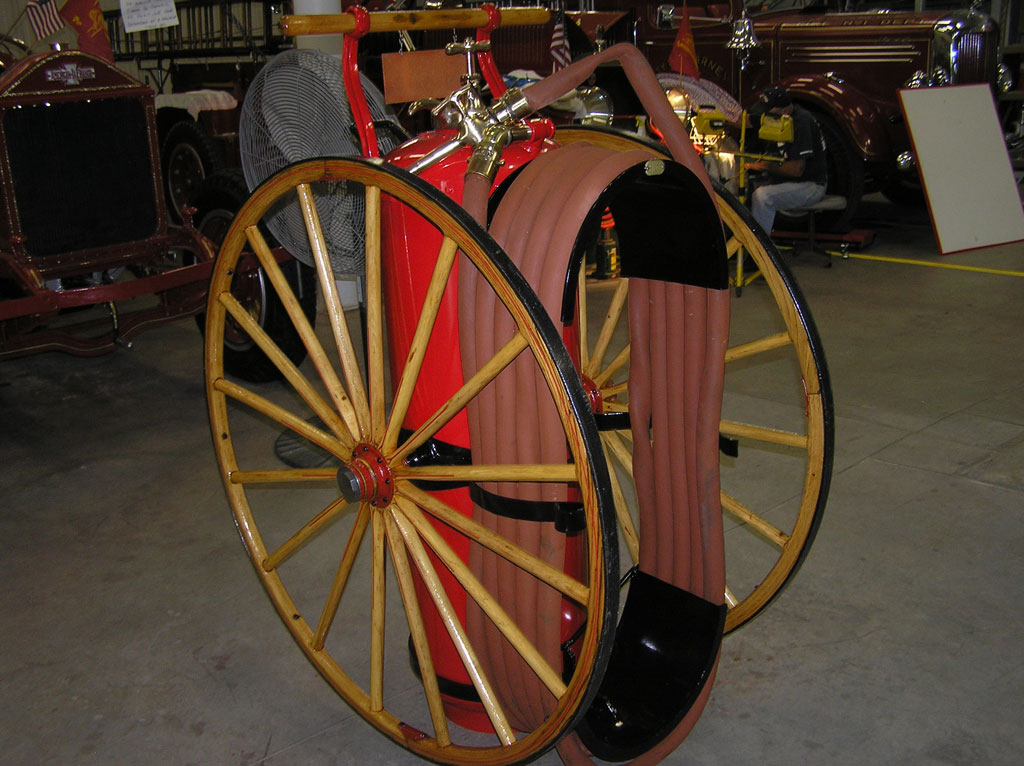
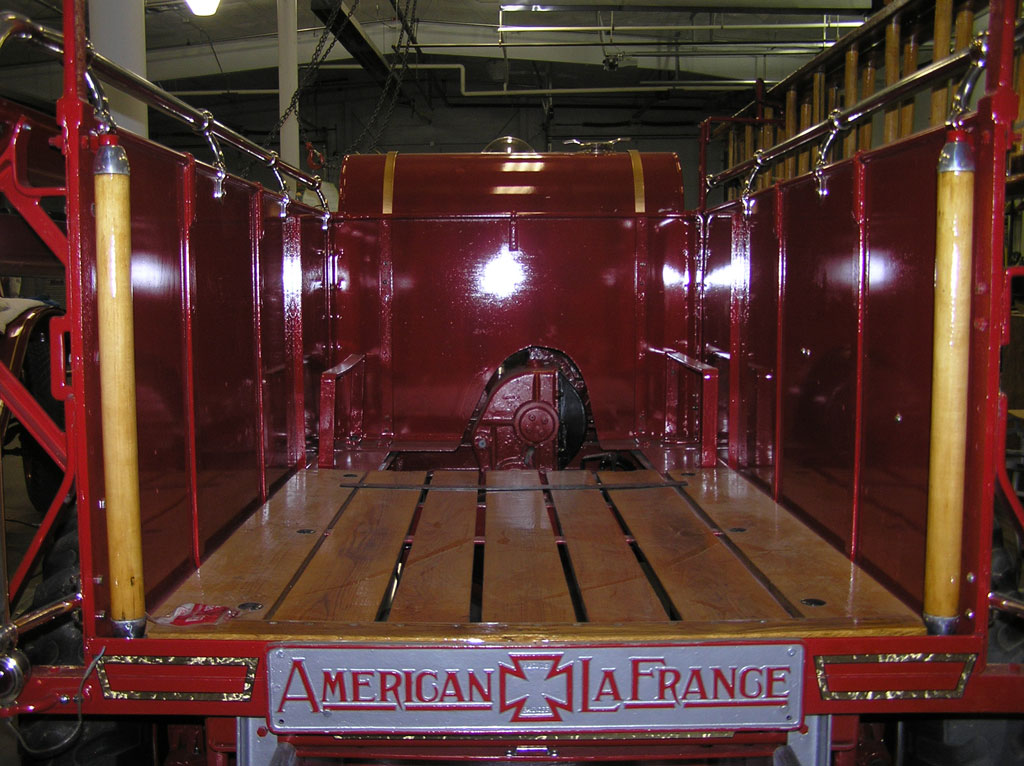
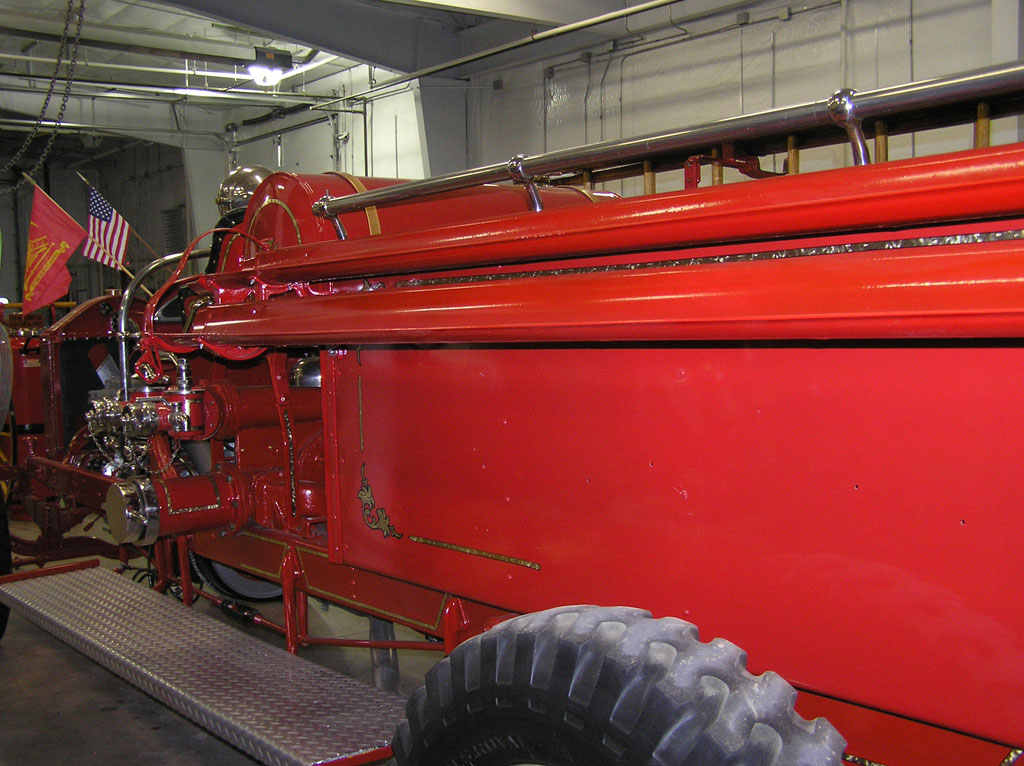
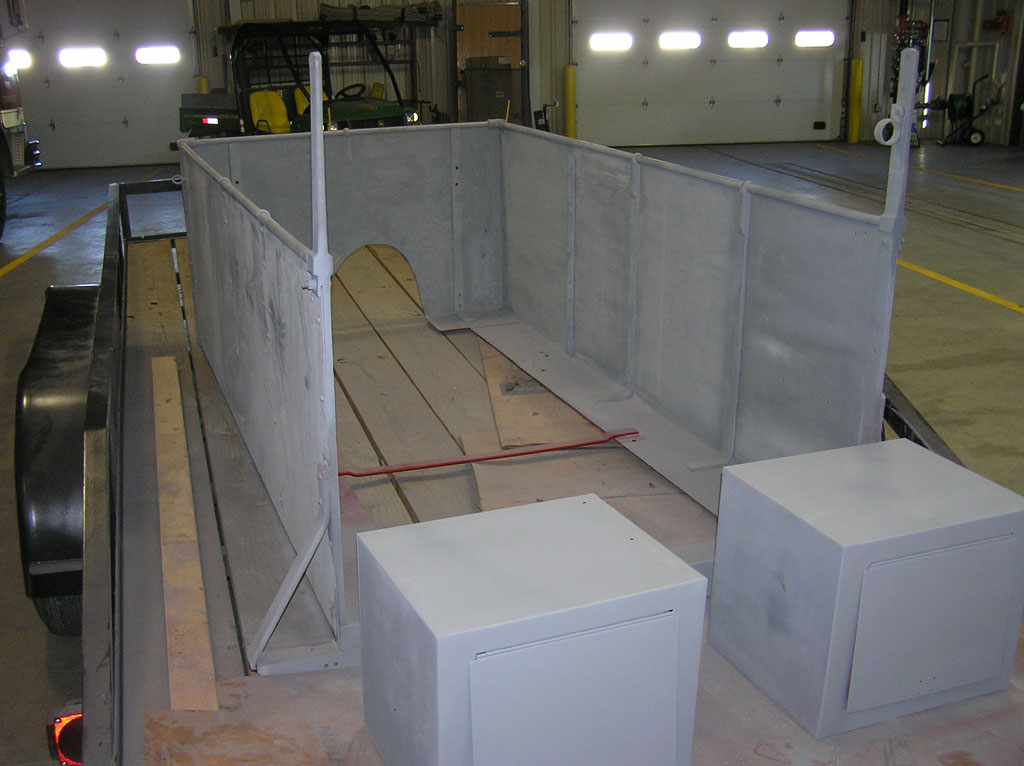
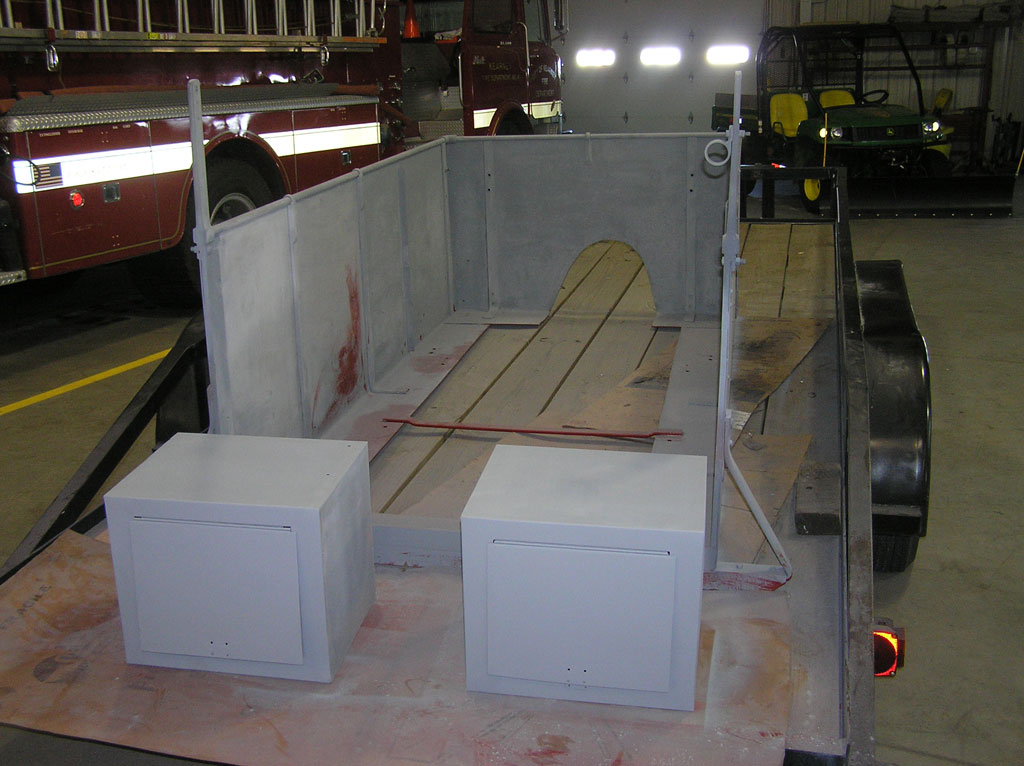
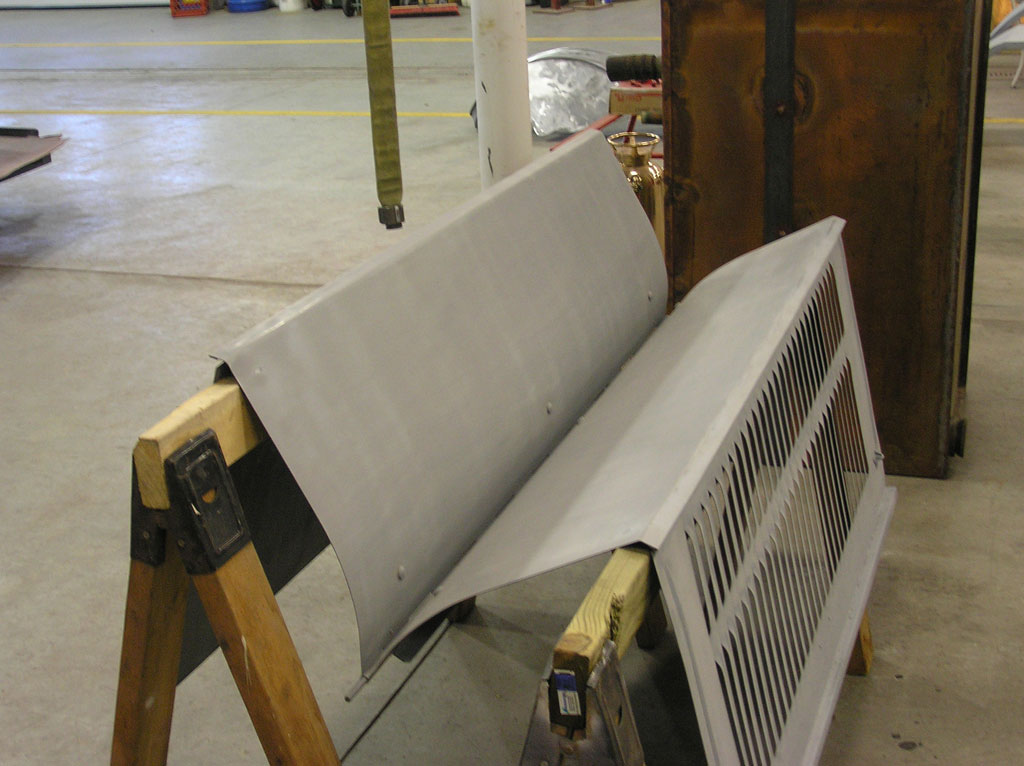
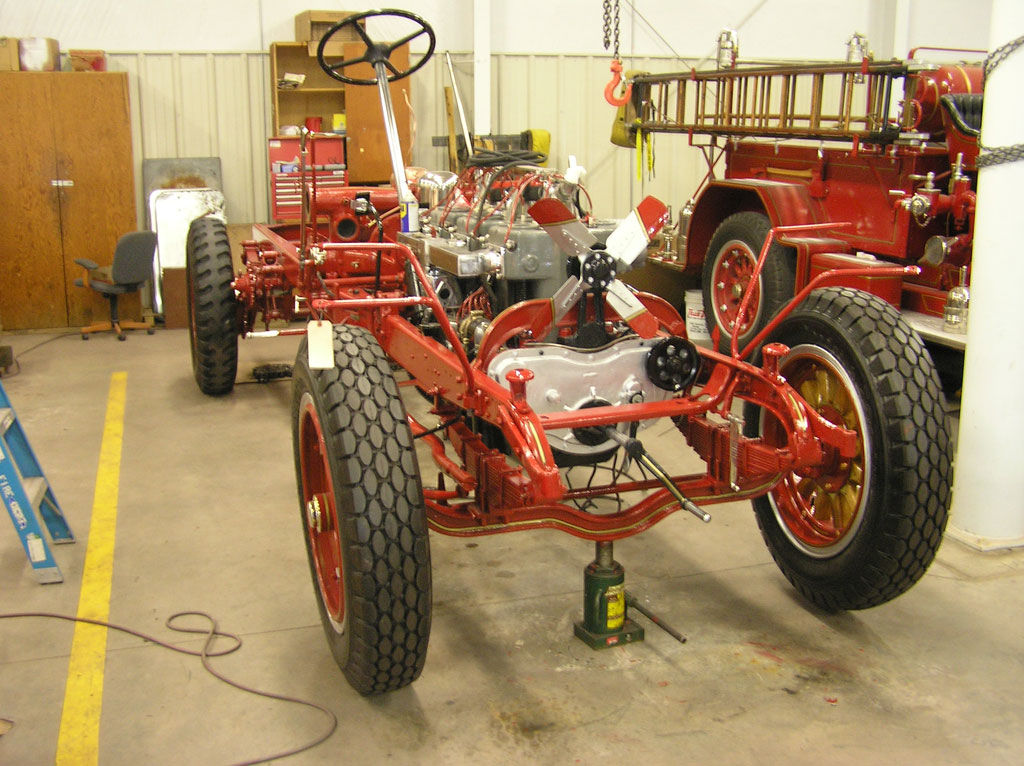
Before Burnoff (Restoring the American LaFrance)
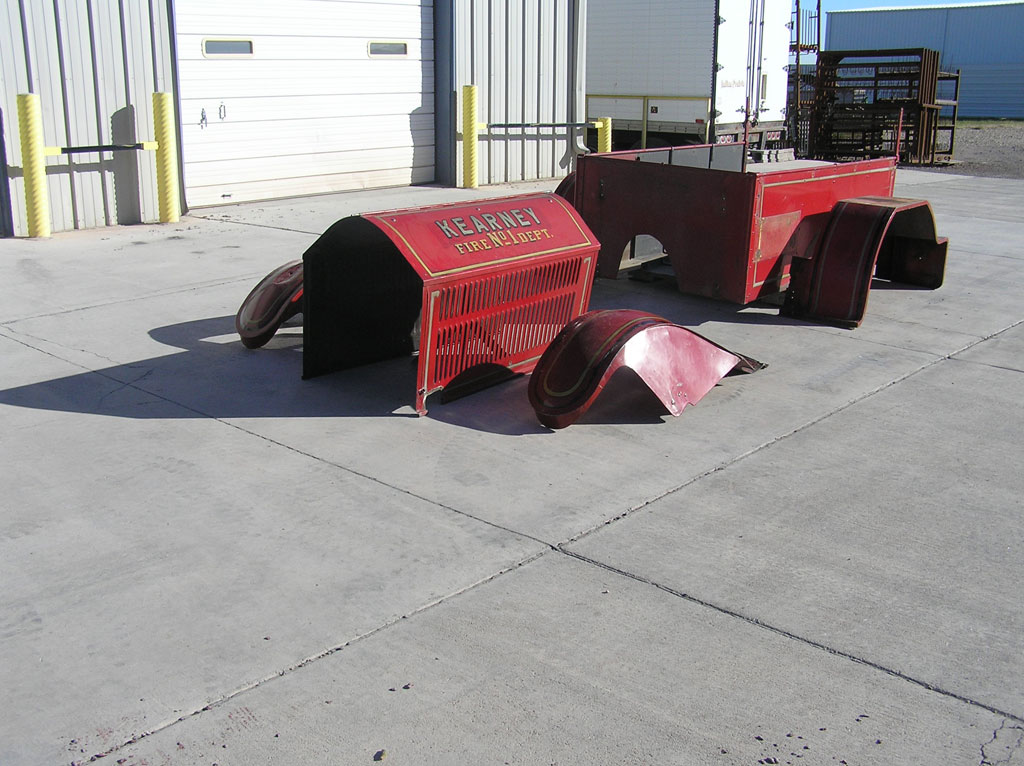
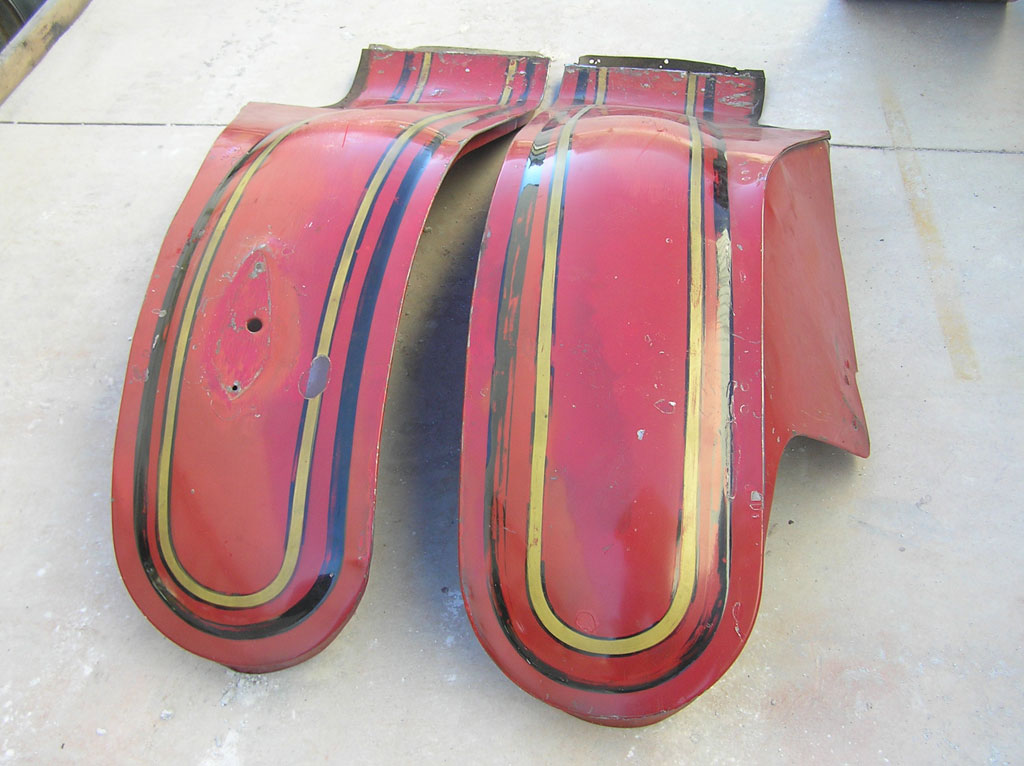
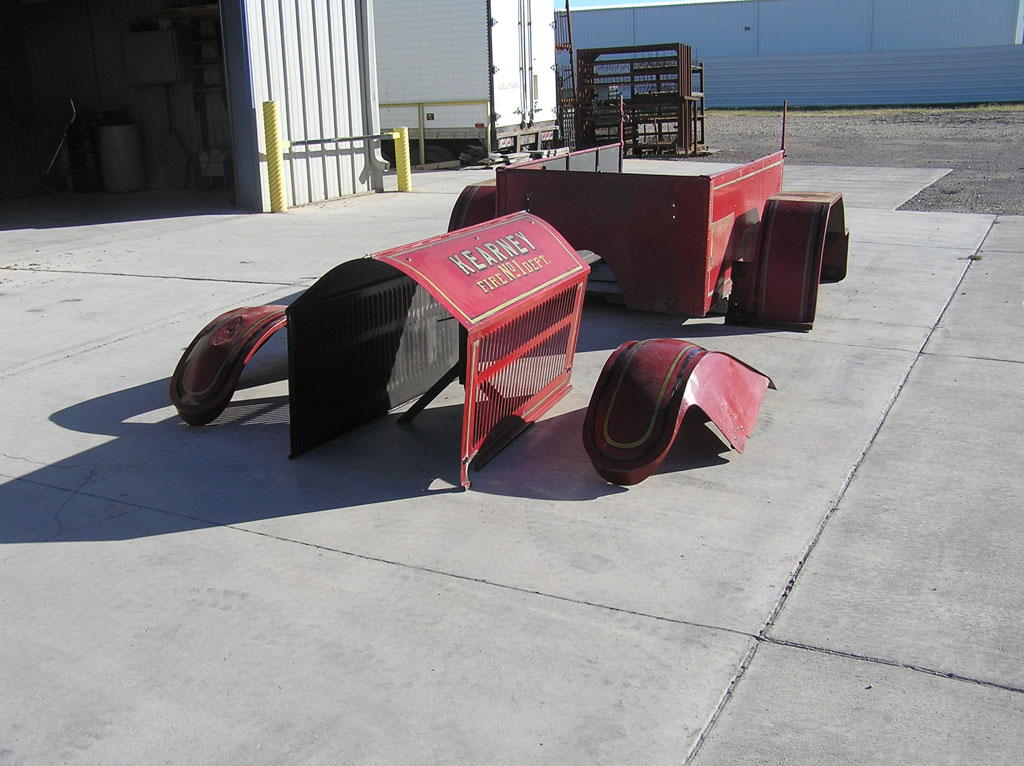
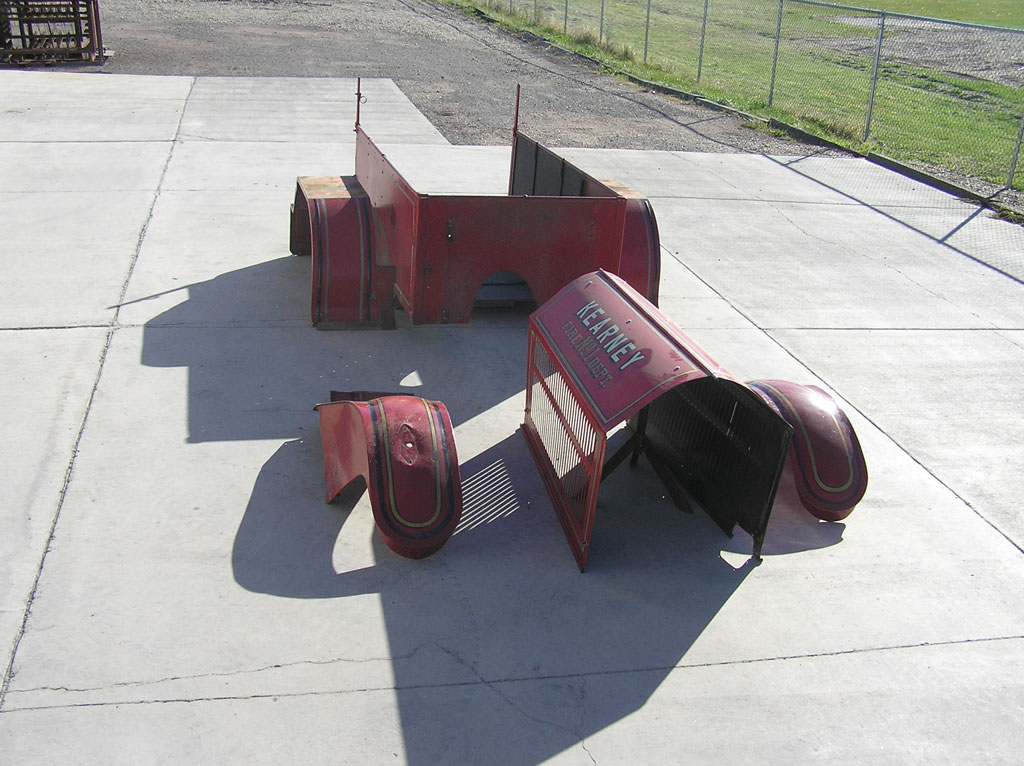
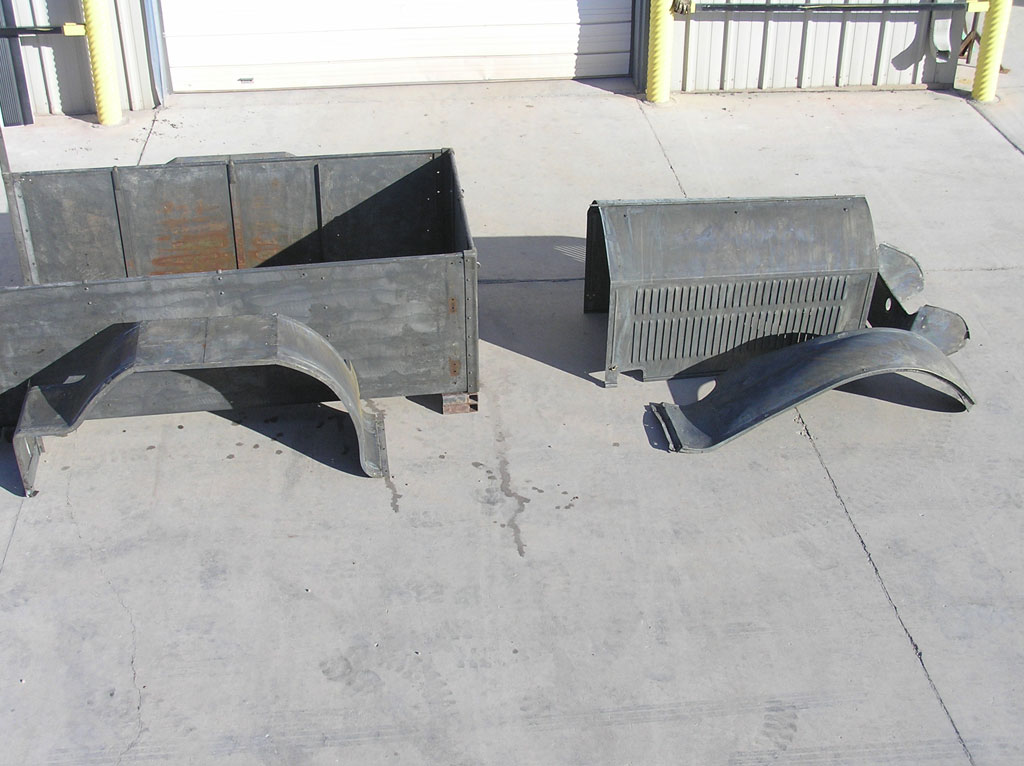
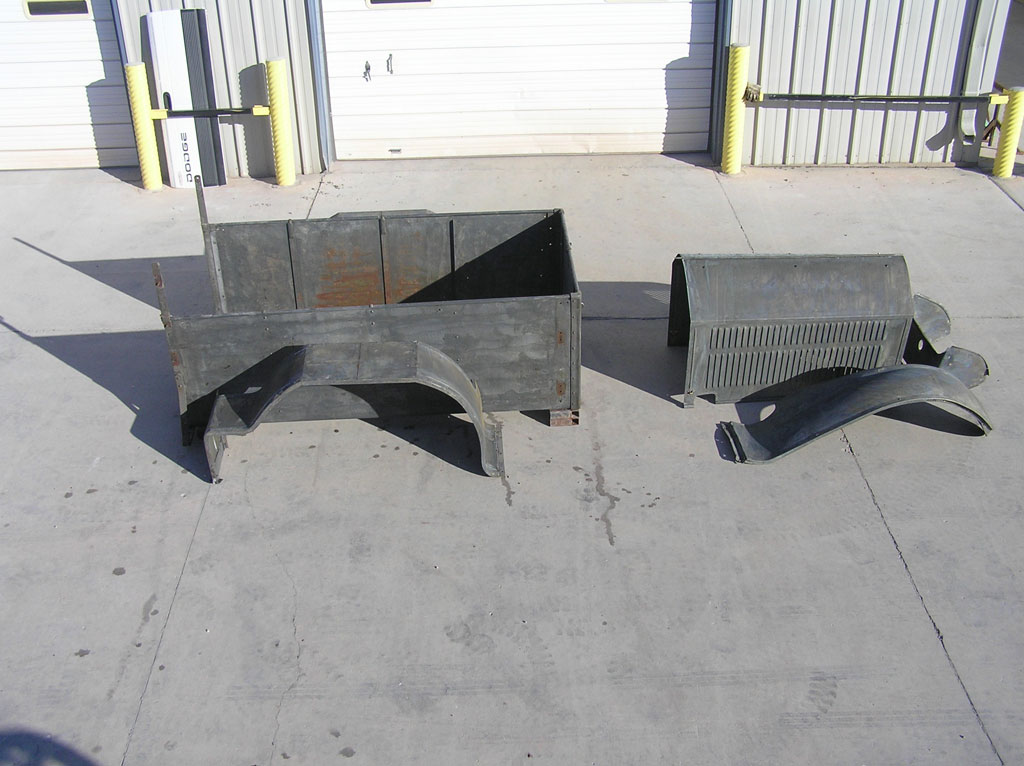
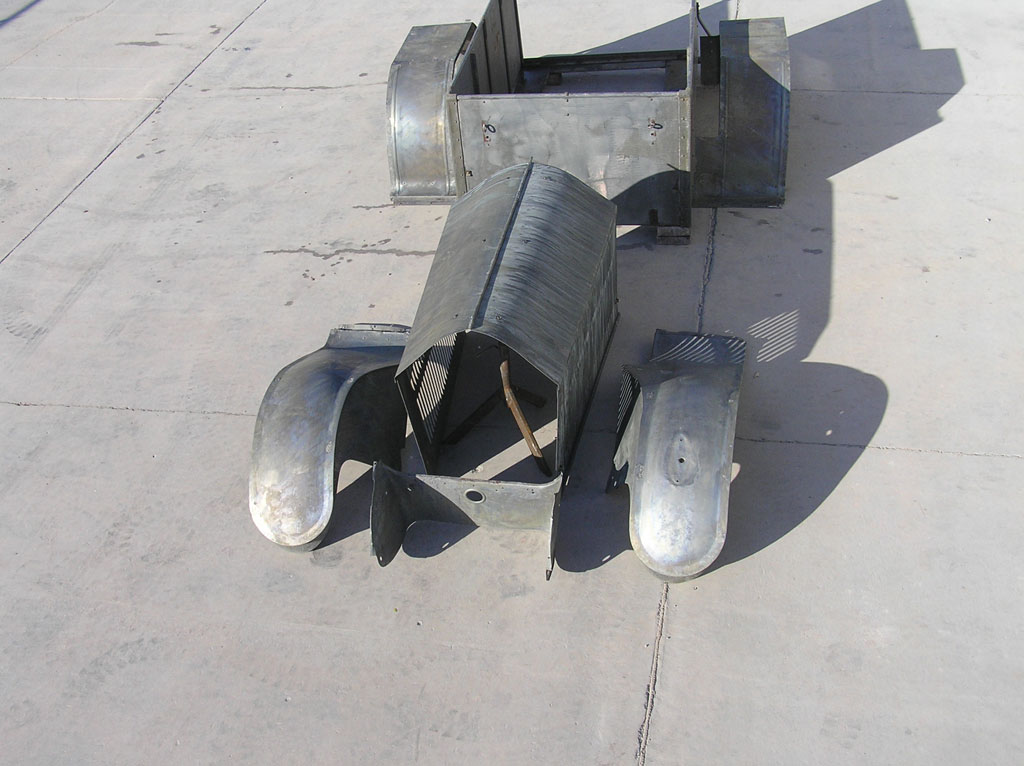
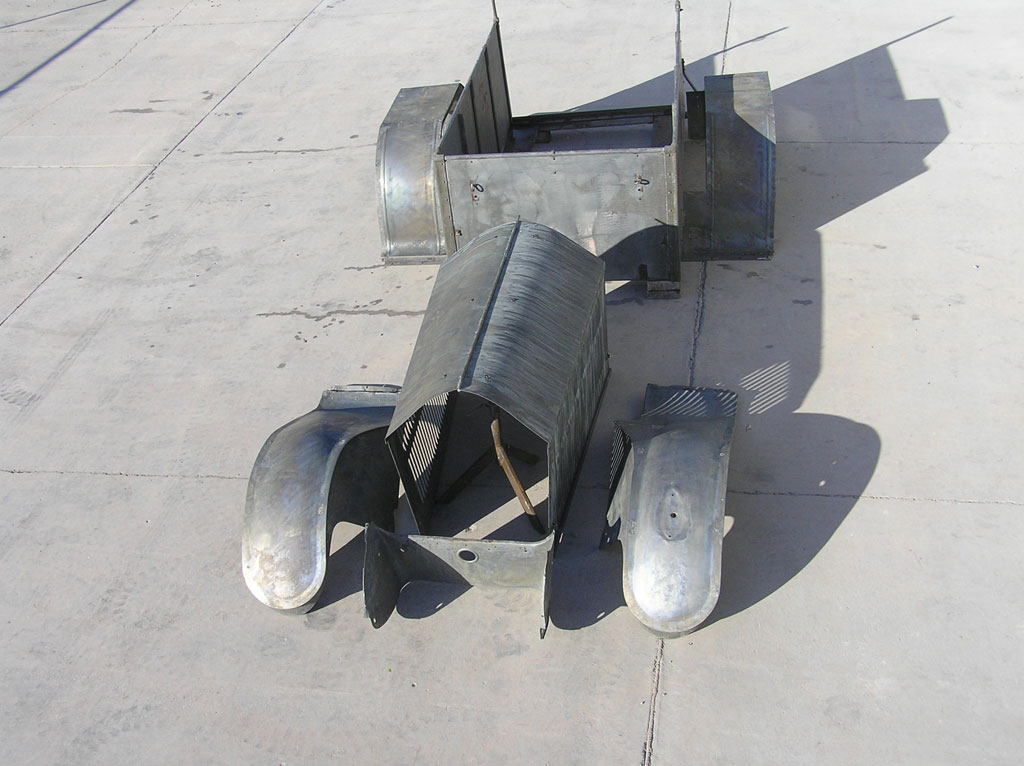
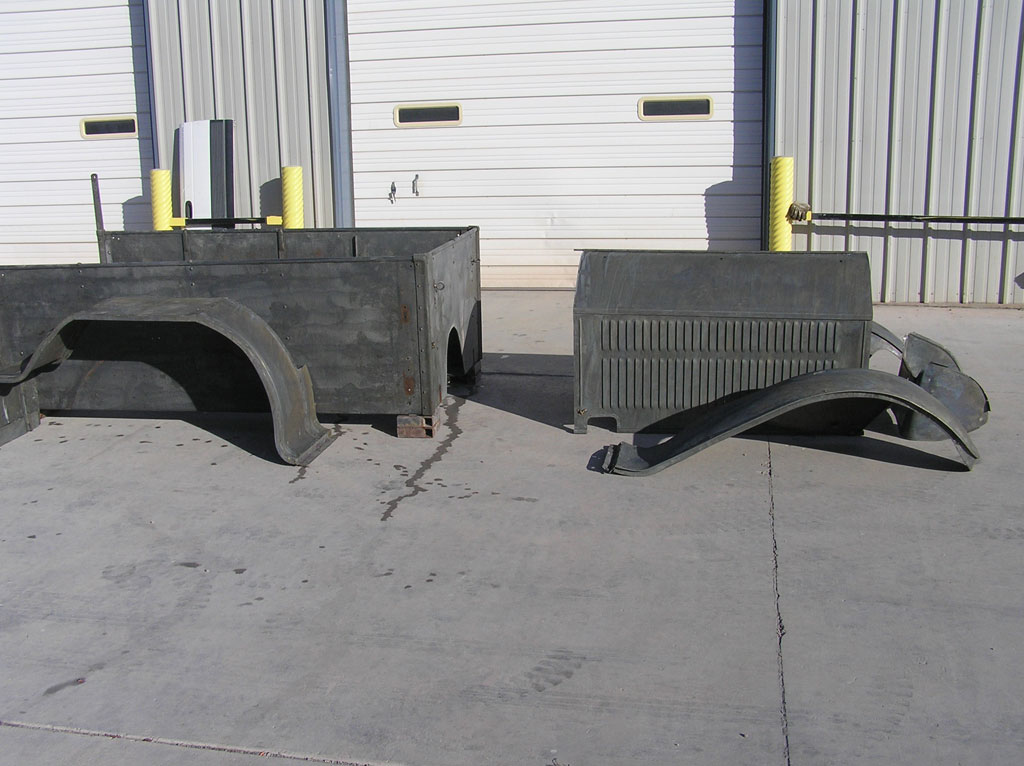
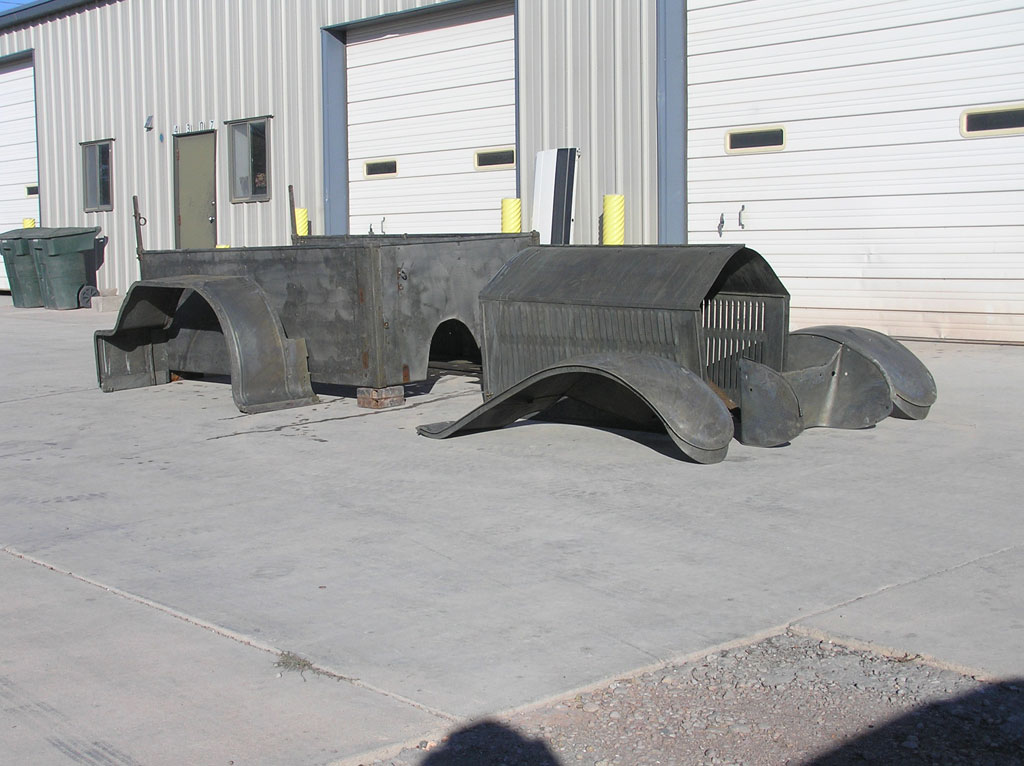
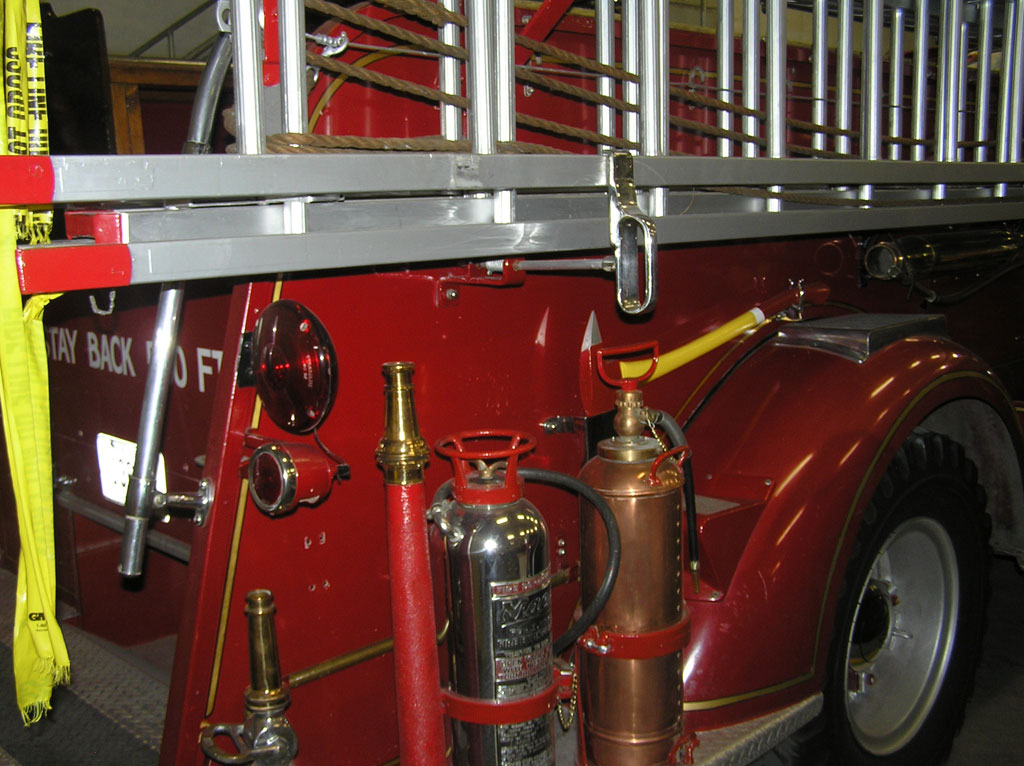
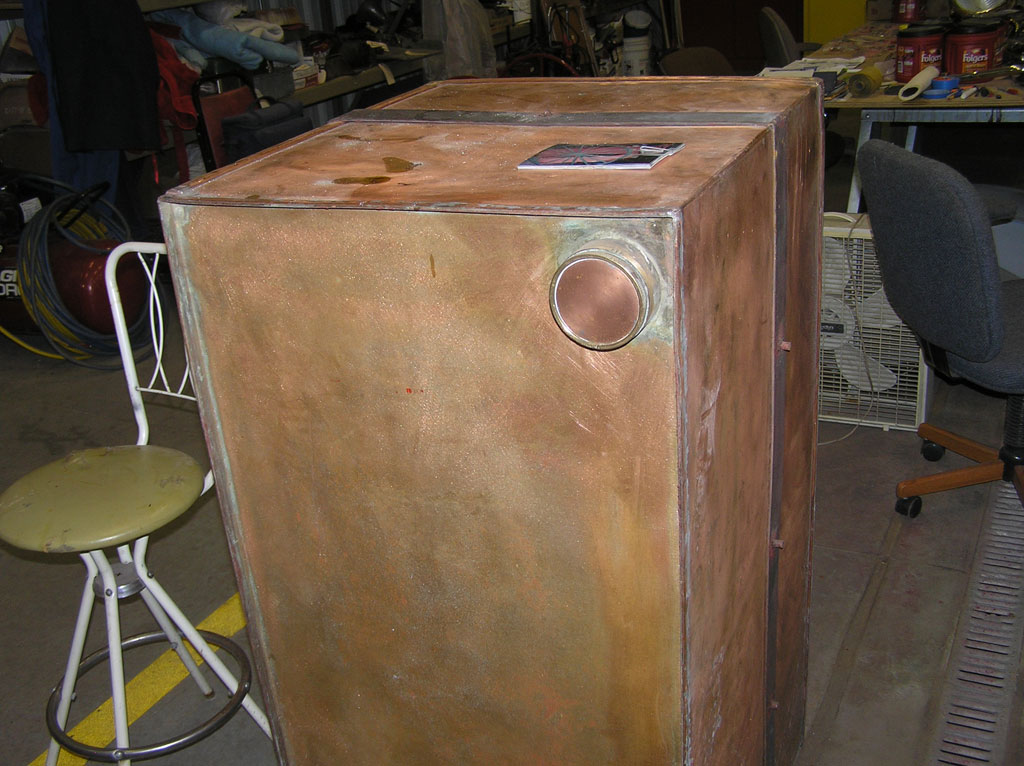
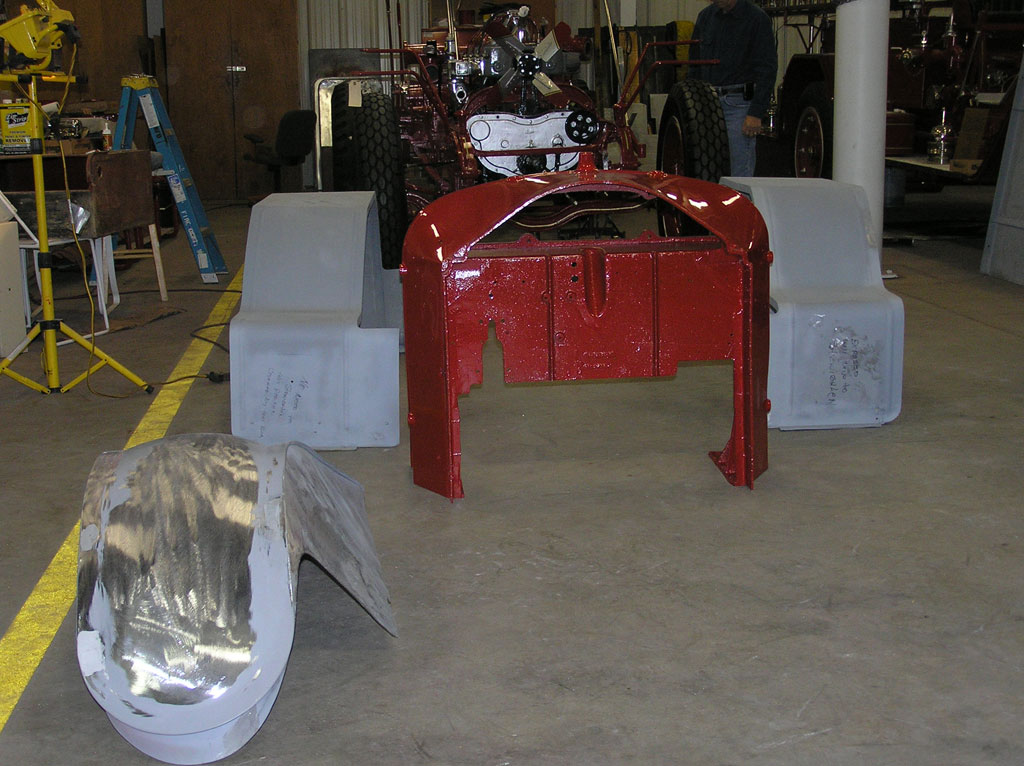
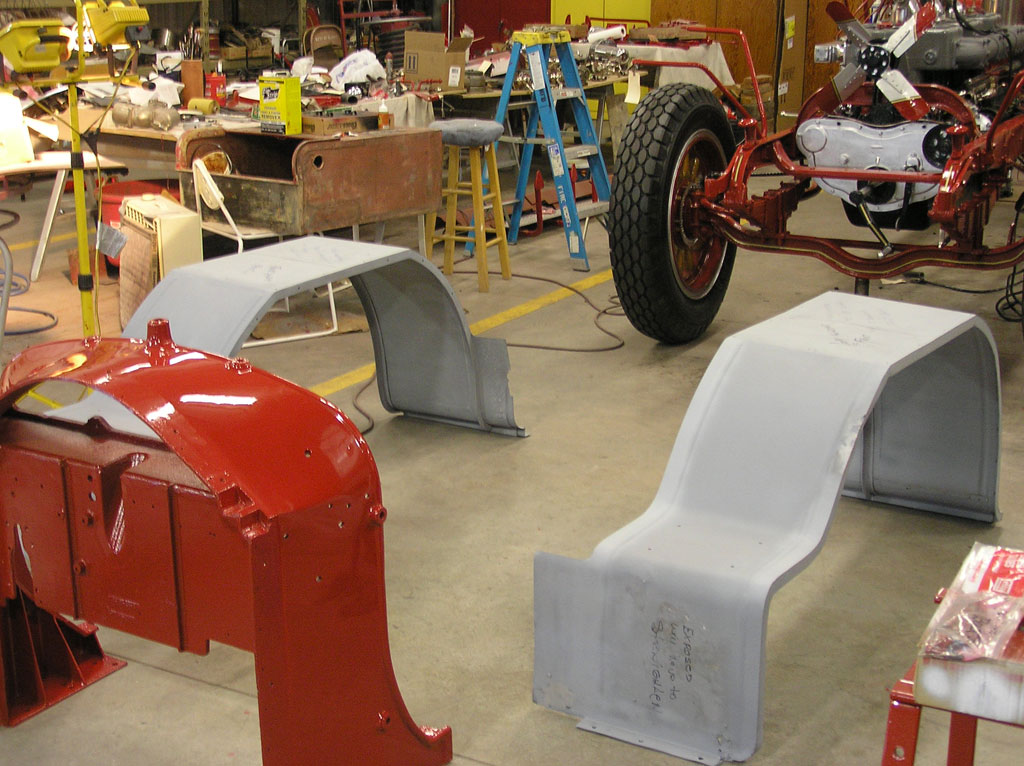
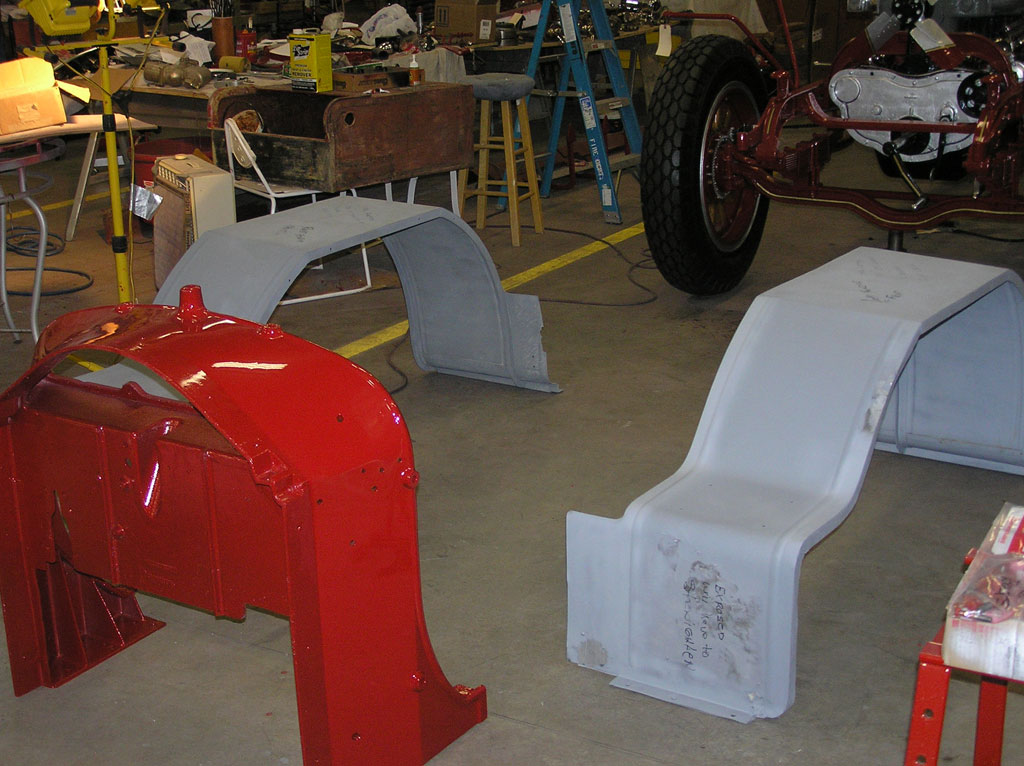
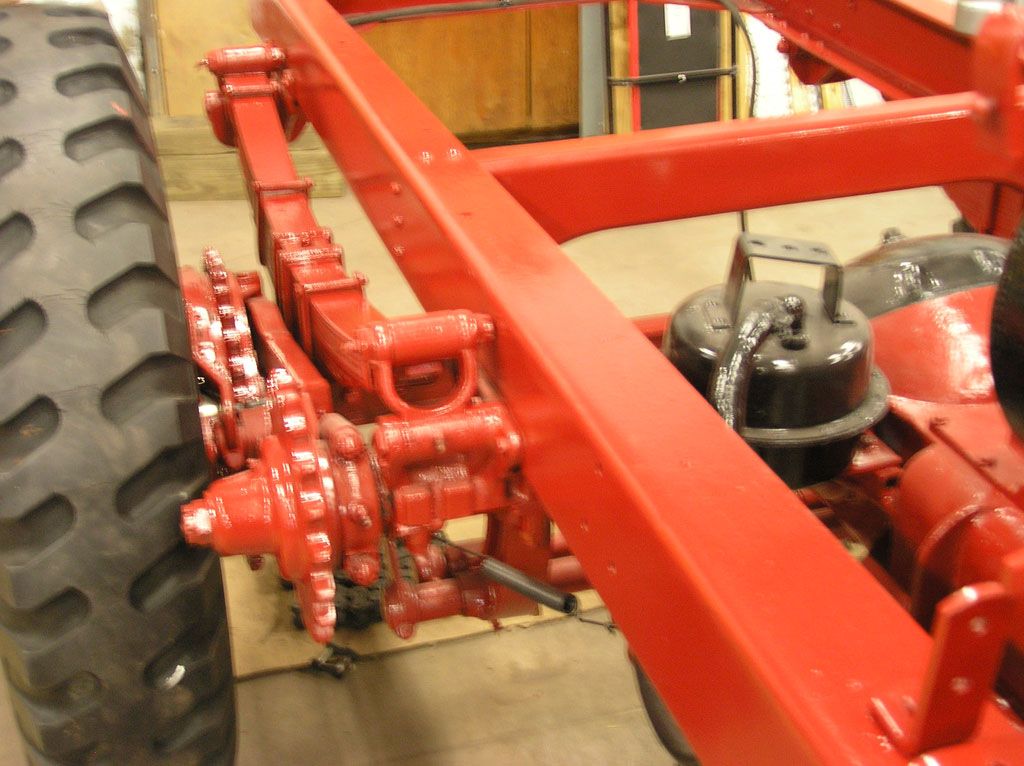
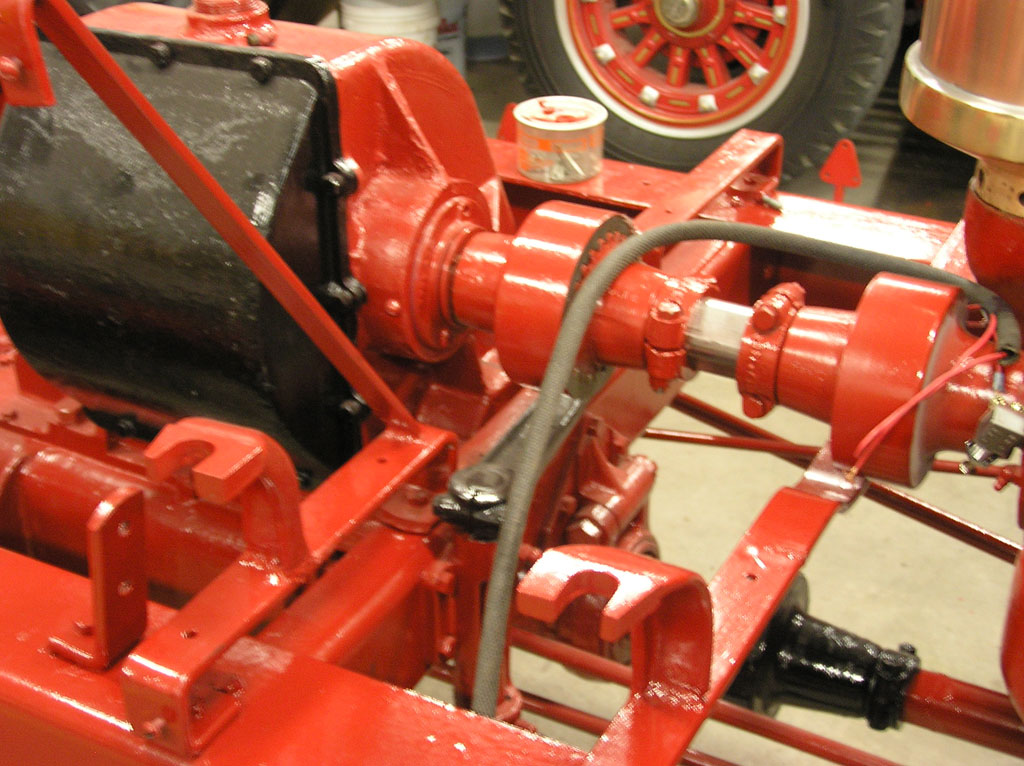
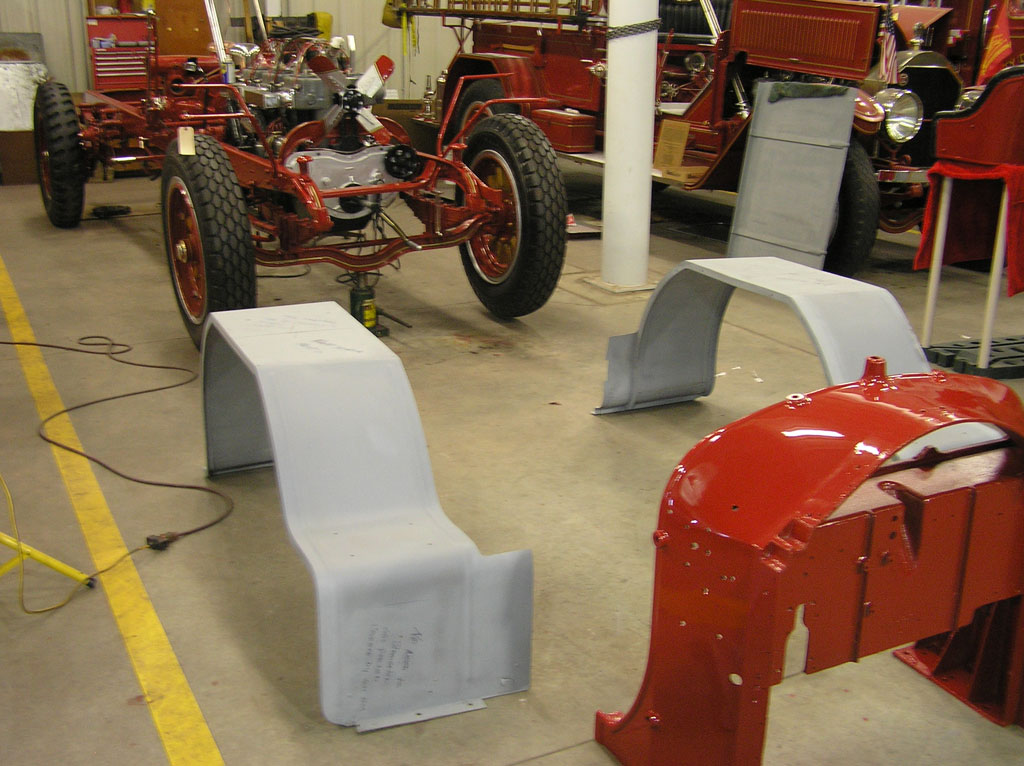
After Burnoff (all paint removed)
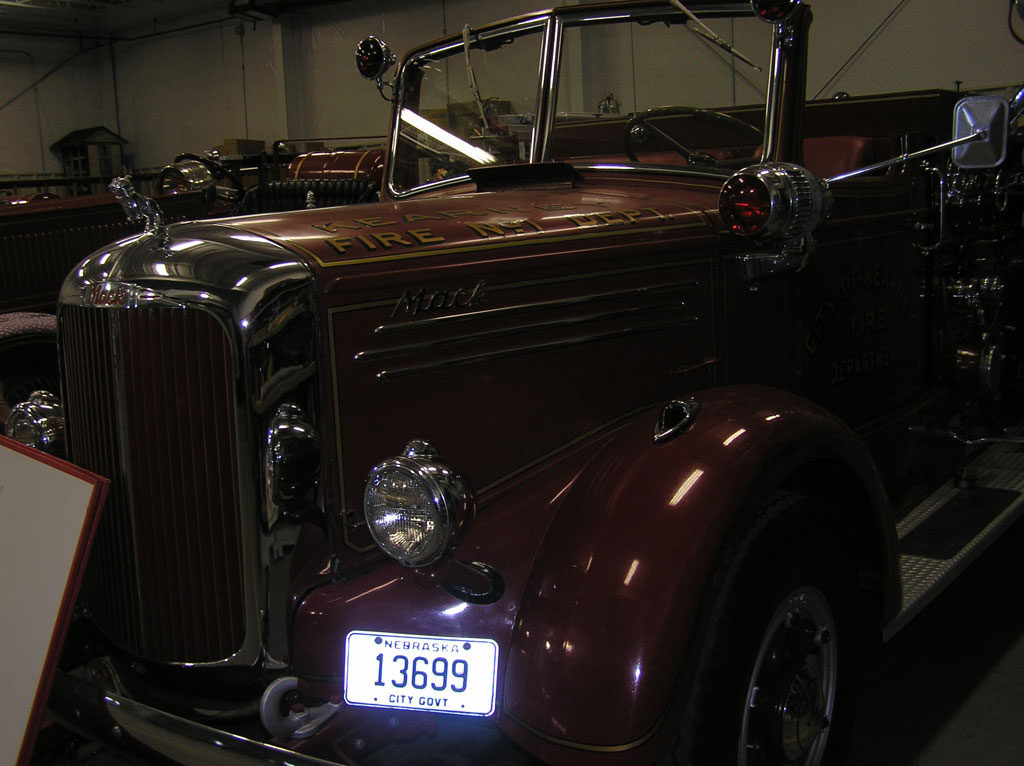
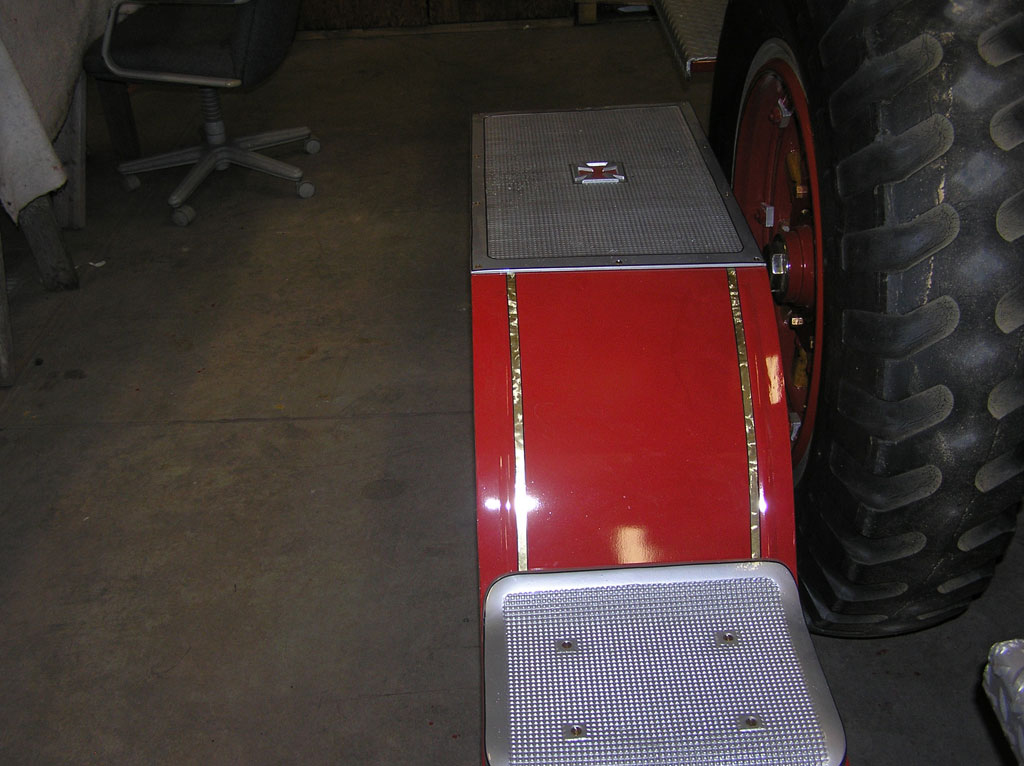
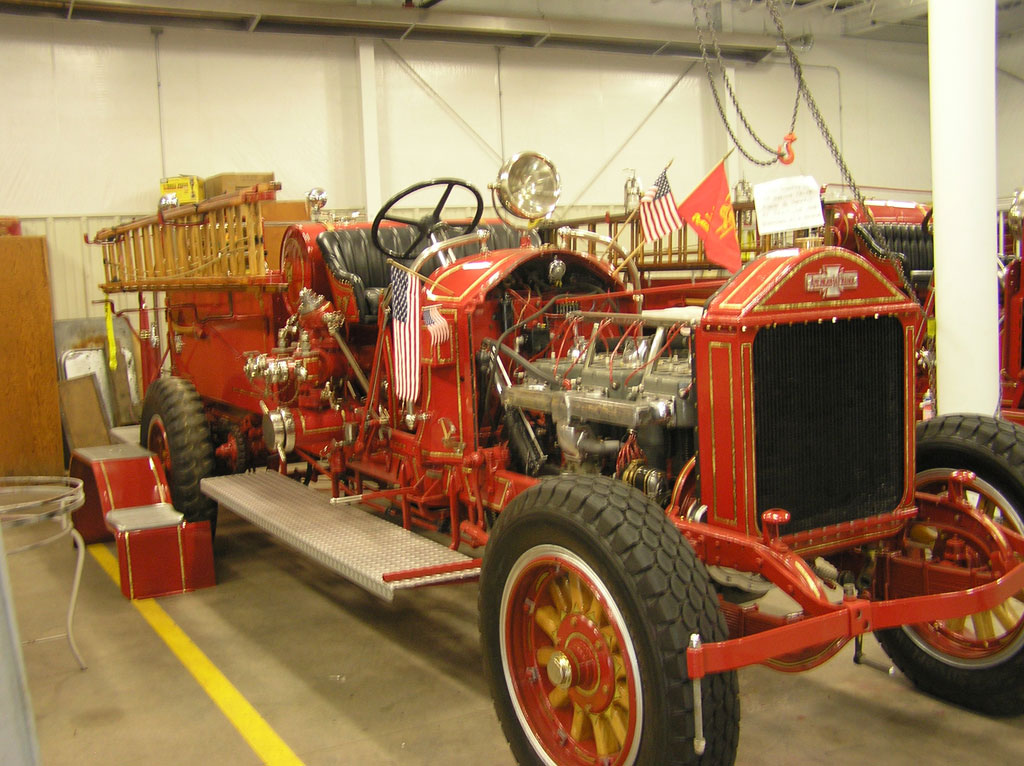
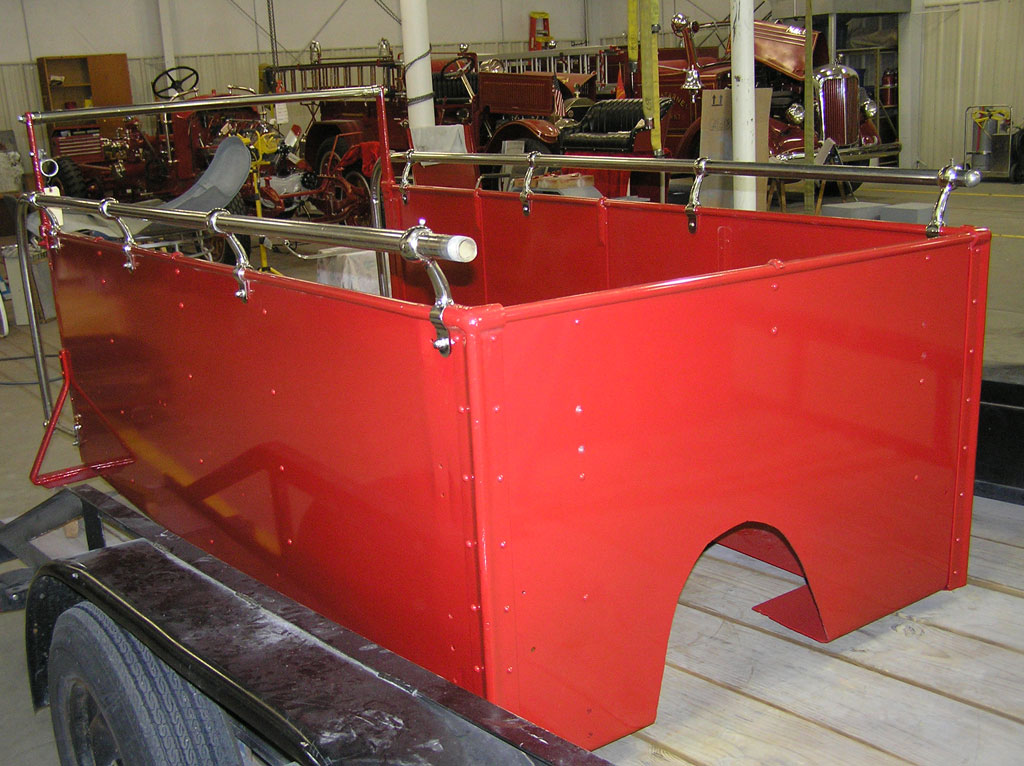
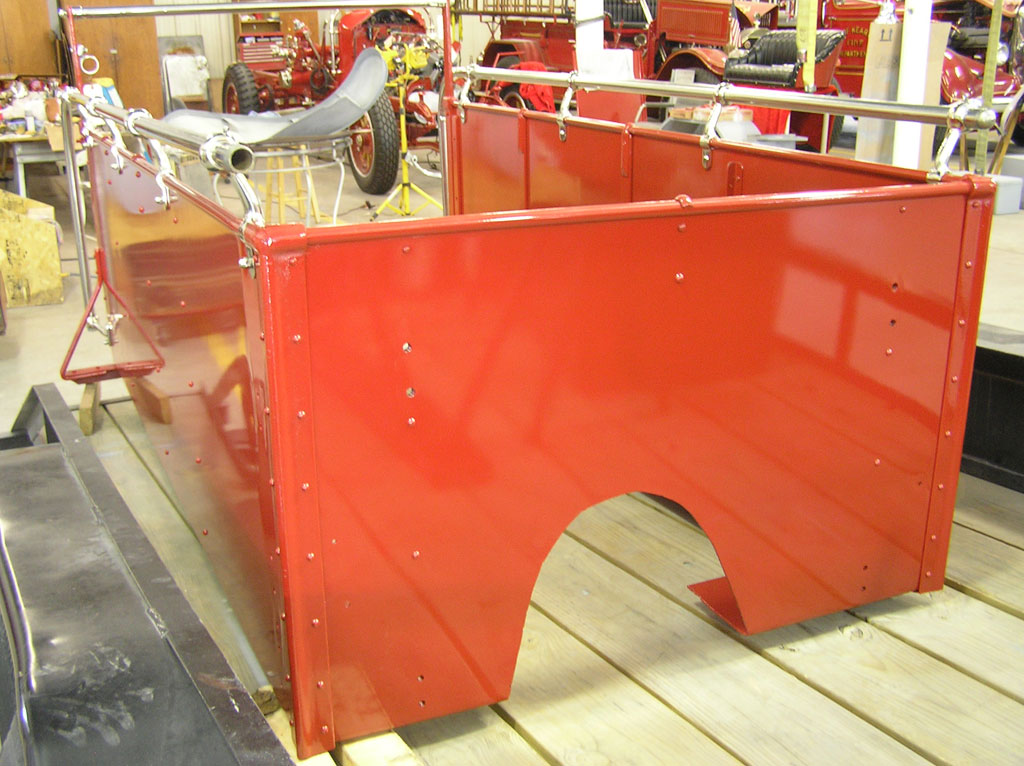
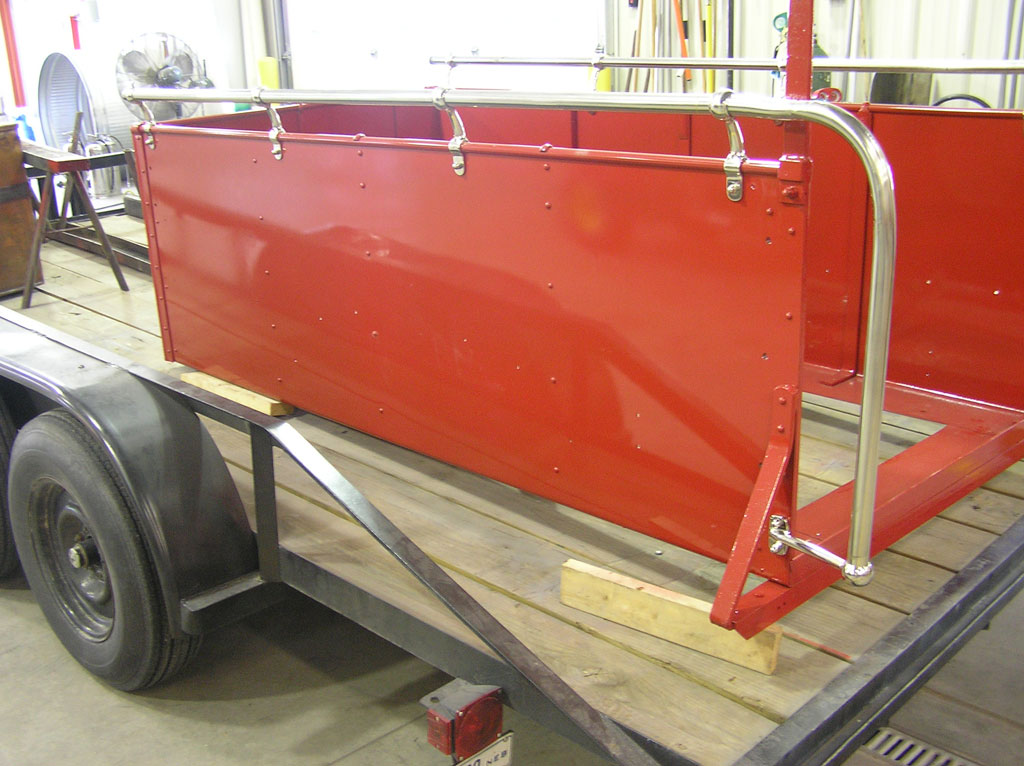
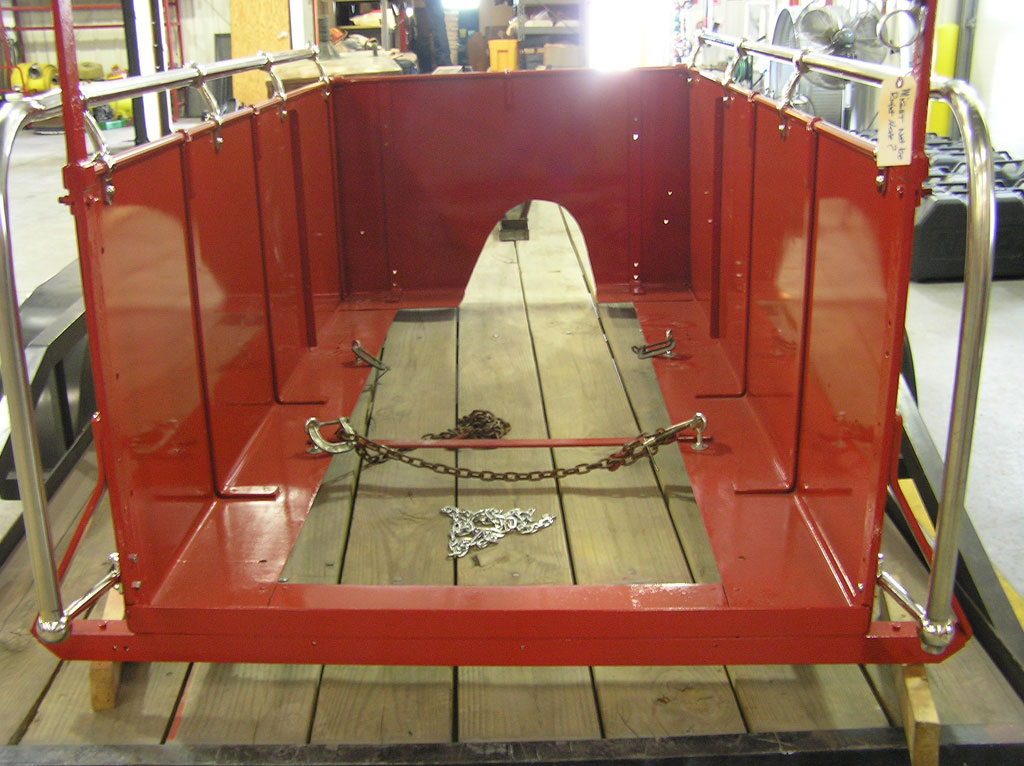
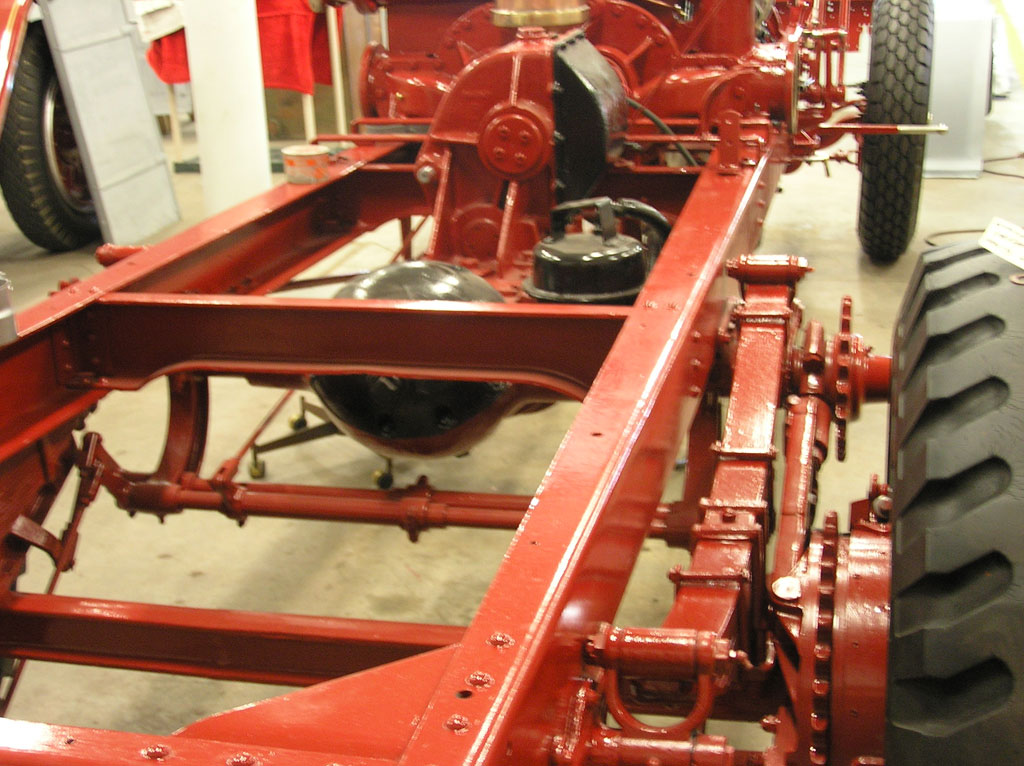
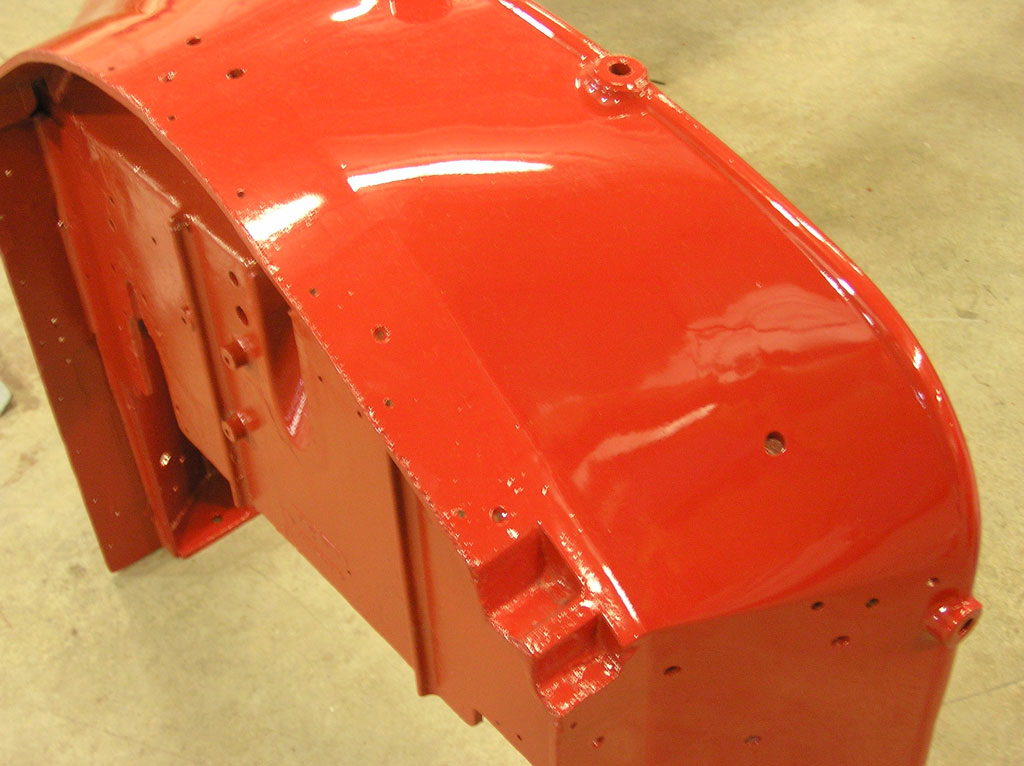
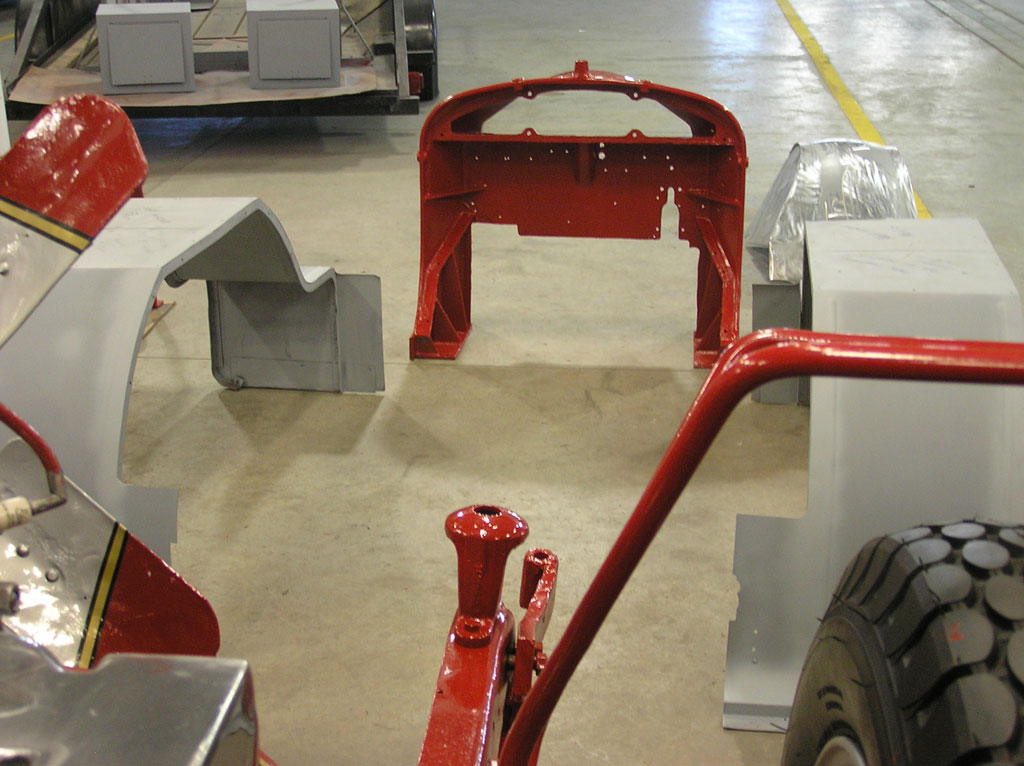
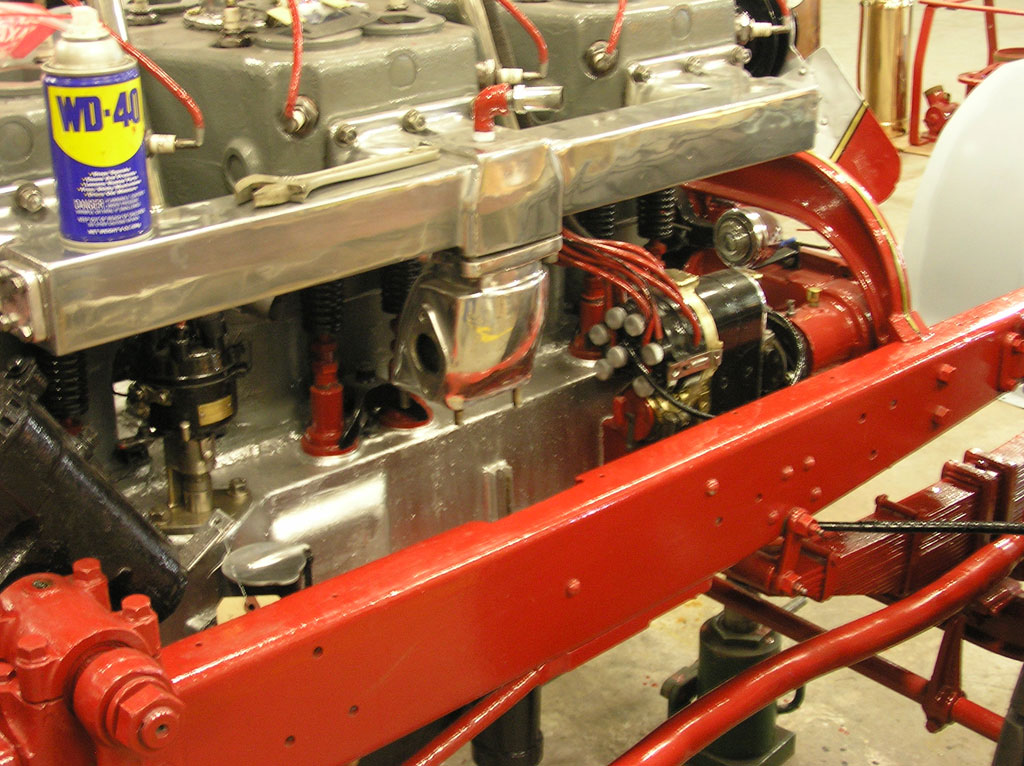
After Painting, Reassembly for Museum

Applications
They are gaining acceptance in the automotive parts rebuilding industry and more recently in the plastics industry as the most economical method of cleaning metal parts. The emissions from burn-off ovens are quite low and the small amount of ash generated can usually go in the trash. With burn-off ovens environmental impact is minimized and operator safety is maximized.
Credit: Carlton Mann is Engineering Manager – Cleaning Ovens at Steelman Industries, P.O. Box 1461, Kilgore, TX 75663; 903/984-3061.